CME for
KSGE members
Kim, Kim, and Kim: A Rare Cause of Subepithelial Tumor in the Gastric Fundus
Quiz
A 46-year-old woman presented with a gastric subepithelial tumor. The tumor was incidentally detected during a screening endoscopy. The tumor was located on the posterior wall of the gastric fundus, without any observable erosion or ulceration on its surface ( Fig. 1A). When compressed using biopsy forceps, the tumor felt hard and partially fixed. On endoscopic ultrasonography, the tumor measured 0.8 cm in diameter and presented as a heterogeneously hypoechoic lesion in the submucosal layer ( Fig. 1B). Examination of the specimen obtained from the endoscopic biopsy revealed only chronic gastritis. The patient underwent a follow-up endoscopy 2 years later, which revealed that the tumor size had increased ( Fig. 1C). Therefore, traction-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection was performed ( Fig. 1D- F). What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer 
Histopathological examination of the resected specimen revealed spindle cell proliferation, and infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells with fibroedematous stroma, in the submucosal layer ( Fig. 2A). The spindle cells were immunopositive for CD34 ( Fig. 2B) and immunonegative for c-kit, smooth muscle actin, and S-100 protein. Based on these findings, an inflammatory fibroid polyp (IFP) of the stomach was diagnosed. Because the tumor was completely resected, further treatment was not pursued. No recurrence was observed on follow-up endoscopy one year later. IFPs are rare, benign, mesenchymal tumors occurring throughout the gastrointestinal tract, and they are most commonly found in the gastric antrum [ 1]. Although the pathogenesis and etiology of IFPs remain unclear, an association with local inflammatory response caused by injury, infection, or metabolic triggers has been suggested [ 2]. The typical endoscopic findings are semi-pedunculated, subepithelial tumors covered by normal mucosa, often with ulceration, in the gastric antrum. Although IFPs are generally considered benign lesions, it is challenging to diagnose before resection, similar to other mesenchymal tumors located in the submucosa or muscularis propria [ 3]. Therefore, endoscopic resection and surgical resection are sometimes performed for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes [ 4]. In the present case, the tumor was located at the gastric fundus, a rare location for IFPs, and its size had increased during the follow-up. Therefore, a malignant lesion, such as a neuroendocrine tumor or gastrointestinal mesenchymal tumor, was suspected. Traction-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection was performed to provide adequate visualization, facilitating a complete and safe submucosal dissection.
Fig.Т 1.
(A) Initial endoscopy reveals a small subepithelial tumor on the posterior wall of the gastric fundus. (B) On endoscopic ultrasonography, the tumor presents as a heterogeneously hypoechoic lesion in the submucosal layer, measuring 0.8 cm in diameter. (C) On follow-up endoscopy 2 years later, the tumor has increased in size although no erosion or ulceration is noted. (D) Traction-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection is performed. (E) The tumor is removed completely. (F) The inner surface of the resected specimen. 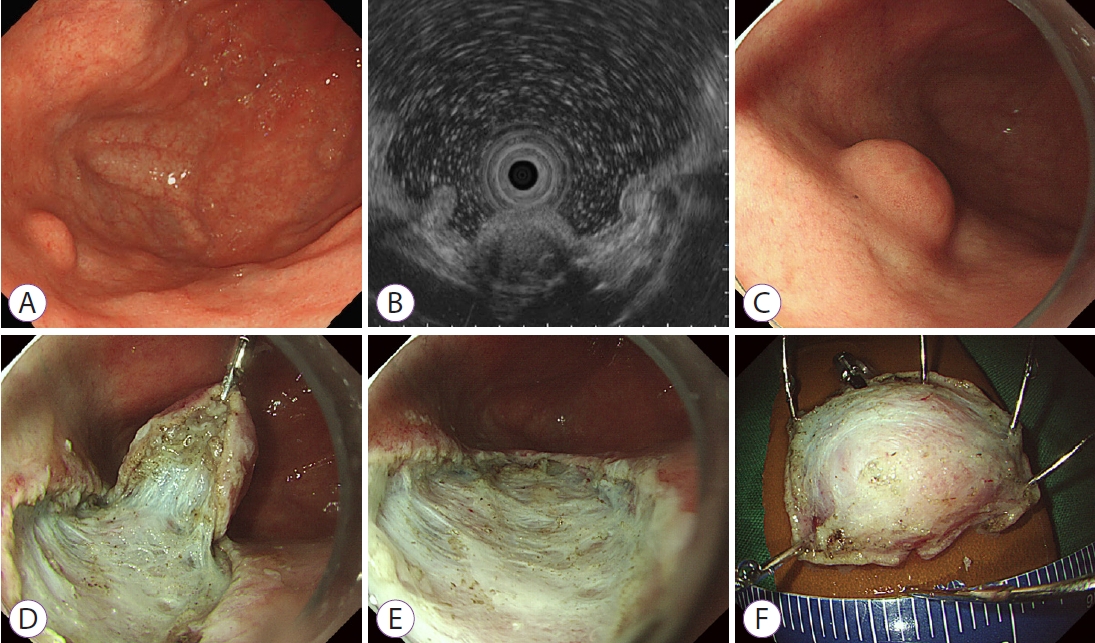
Fig.Т 2.
(A) Histopathological examination reveals spindle cell proliferation and infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells in the submucosal layer (hematoxylin & eosin stain, У200). (B) The spindle cells are immunopositive for CD34, and immunonegative for c-kit, smooth muscle actin, and S-100 protein (CD34 stain, У100). 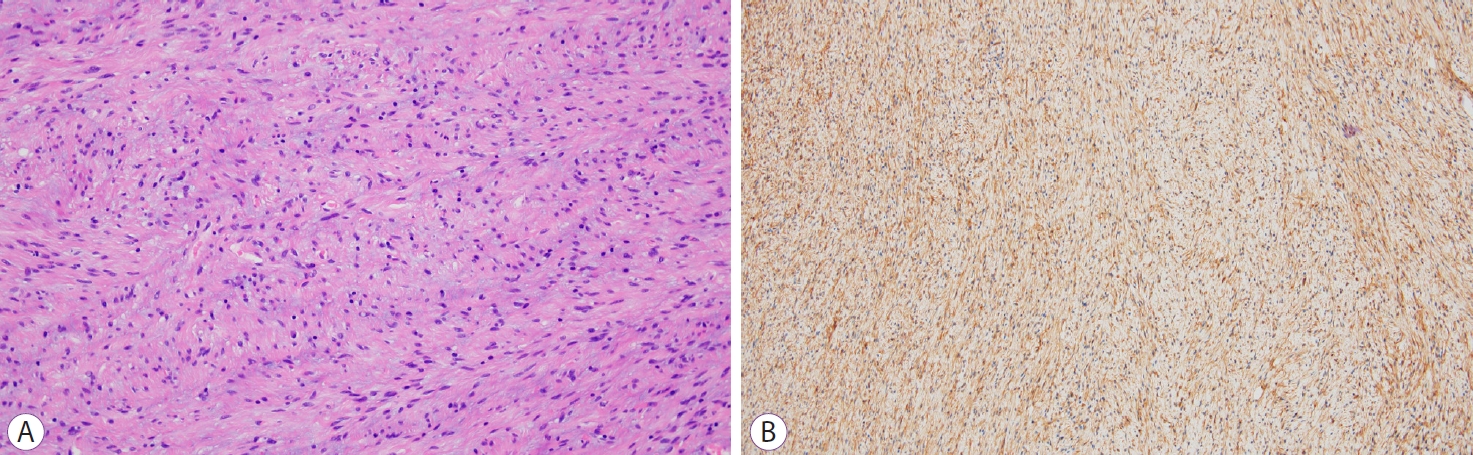
REFERENCES
1. Albuquerque A, Rios E, Carneiro F, Macedo G. Evaluation of clinico-pathological features and Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric inflammatory fibroid polyps. Virchows Arch 2014;465:643т647.  
|
|











