INTRODUCTION
The technique of intraductal ultrasonography (IDUS) of the bile duct with a thin-caliber probe and a ropeway system has provided excellent detailed images of the bile duct1 and periductal structures and is an easy transpapillary approach. In addition, once the guide wire is inserted into the bile duct, IDUS and transpapillary biopsy after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) can be performed in a single session. IDUS is used in the differential diagnosis between benign and malignant biliary diseases and assessment for the longitudinal extension of cholangiocarcinoma (CC). IDUS has also been reported to be superior to ERCP in the detection of bile duct stones.2
Although useful for the preoperative histological diagnosis and evaluation of the longitudinal extent of CC, percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy and biopsy require considerable time and pose a risk of cancer dissemination.3 Transpapillary biopsy and IDUS are expected to be alternatives to percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy and biopsy for the preoperative histological diagnosis and estimation of the longitudinal extent of CC.4,5 In this review, we discuss the usefulness of IDUS in the diagnosis of CC.
We have reported that IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) shows various cholangiographic features similar to those of pancreatic cancer (PCa), primary SC (PSC), and CC.6 The most useful feature for the diagnosis of IgG4-SC is its association with autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP).7 However, several cases of IgG4-SC have reportedly shown no association with AIP, and such cases are particularly difficult to distinguish. 8 Because of the establishment of the concept of AIP, unnecessary surgeries can be avoided in the event of misdiagnosis of PCa. Similarly, if a diagnosis of IgG4-SC can be established, then both liver transplantation under a diagnosis of PSC and hepatectomy under a diagnosis of bile duct cancer can both be avoided. Recently, we have established a diagnostic criterion for IgG4-SC on the basis of a cholangiographic classification.9 We classified IgG4-SC patients into three groups on the basis of cholangiographic features in order to distinguish them from PCa, PSC, and CC, respectively. Our diagnostic criteria for IgG4-SC were established in a comparative study of the clinical, imaging, serological, and histopathological features and other organ involvement for each group. We also focused on the role of IDUS in the diagnosis of IgG4-SC in this review.10
IMAGING BY IDUS
In the intrapancreatic bile duct, IDUS demonstrates the bile duct wall as a low echoic layer and the pancreatic parenchyma as a fine reticular pattern.11 In the extrahepatic-extrapancreatic bile duct, IDUS findings show a two-layer structure: 1) an inner echo-poor layer and 2) an outer echo-rich layer. Using IDUS, the portal vein adjacent to the common bile duct can be seen and the right hepatic artery is visible between the bile duct and the portal vein in the hepatic hilum.11
THE ROLE OF IDUS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF CC
Menzel et al.12 proposed the following criteria. Malignancy is suspected when IDUS shows a hypoechoic mass with irregular margins and inhomogeneous low-echo areas invading the surrounding tissue. On the other hand, homogeneous echo patterns and smoothly defined margins are regarded as benign. Tamada et al.13 described an interruption of the bile duct wall structure or a tumor diameter greater than 8.0 mm as being highly suspicious for an underlying malignancy.
The inner hypoechoic layer of the IDUS image corresponds not only to the fibromuscular layer but also to a part of the perimuscular connective tissue.11 Therefore, even though the tumor may be limited to the inner low echoic layer, it may invade the perimuscular connective tissue or may be confined to the fibromuscular layer. Disappearance of the high echoic layer between the tumor and a vessel is regarded as a positive sign of vascular invasion. Using this criterion, the accuracy of IDUS in assessing tumor invasion to the right hepatic artery and portal vein was 93% to 100%.12,14 However, IDUS is significantly inferior to conventional endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) with respect to detection of lymph node metastases.12
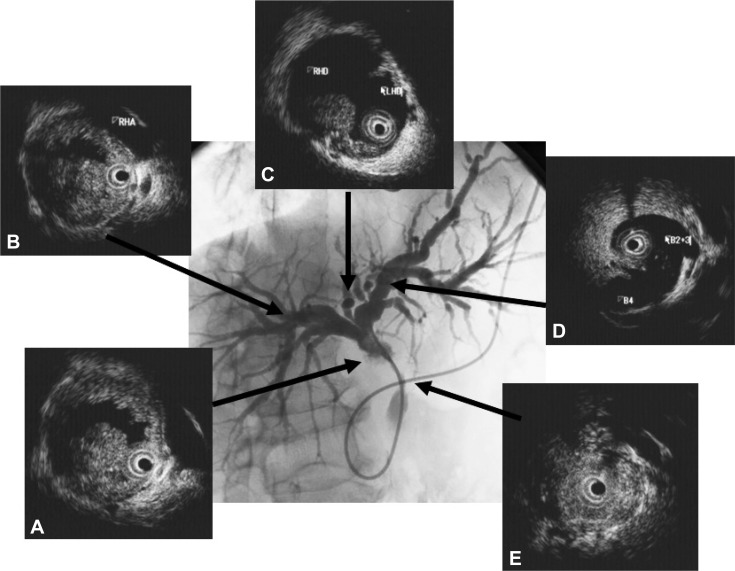
It is important to precisely estimate the longitudinal extent of CC preoperatively for curative surgery. Extrahepatic bile duct cancer frequently shows mucosal and intramural spread longitudinally along the bile duct.15 The pattern of infiltration at the proximal border of resected hilar CC is closely related to the gross tumor type.16 The papillary type and nodular type show intraductal growth and superficial spread. The nodular type and flat type show infiltrating growth and submucosal extension. The length of submucosal extension is usually less than 10 mm. Superficial spread of cancer is seen in more than 10% of cases. A tumor-free proximal resection margin of 5 mm appears to be adequate in hilar CC. In all types of CC, IDUS is recommended for assessing the extent of CC (Fig. 1). It has been reported that percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy and biopsy are required to evaluate the longitudinal extent of bile duct cancer.17 Percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy and biopsy require considerable time and pose a risk of cancer dissemination.3 Transpapillary biopsy and IDUS are expected to be alternatives to percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy and biopsy for the preoperative histological diagnosis and estimation of the longitudinal extent of CC.4,5 At present, IDUS is probably the most useful modality to estimate the longitudinal extent of CC.4,5 Menzel et al.12 have reported that IDUS proved to be accurate in preoperative diagnosing and T staging of malignant biliary strictures, whereas it is not suitable for lymph node staging. IDUS using miniprobes during ERCP exceeds conventional EUS in terms of depiction of bile duct obstruction, diagnostic accuracy, and sensitivity and in the prediction of tumor resectability. In addition, and different to EUS, IDUS can be conveniently performed during ERCP in the same session. Noda et al.5 have reported that the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the assessment of the longitudinal extent of cancer on the hepatic and duodenal side by IDUS were 82%, 70%, 78% and 85%, 43%, 70%, respectively. Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of combination of IDUS and concomitant transpapillary biopsy on the hepatic and duodenal side were 88%, 80%, 85% and 77%, 86%, 80%, respectively. Overestimation of the longitudinal extent of CC by IDUS was mainly due to inflammation and obscure images, especially resulting from collapse of the bile duct on the duodenal side of the tumor, and was corrected by transpapillary biopsy in four of five patients. The authors concluded that IDUS is sufficient on the hepatic side of the tumor, but concomitant transpapillary biopsy is recommended on the duodenal side.
THE ROLE OF IDUS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF IgG4-SC
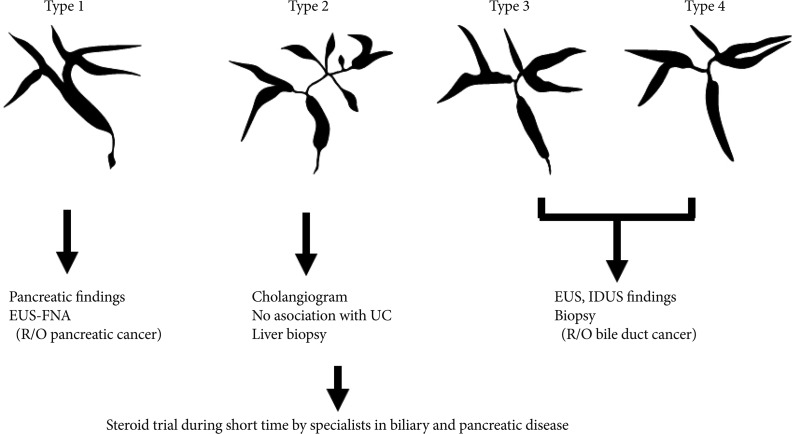
We have reported that IgG4-SC can be classified into four types based on the region of strictures revealed by cholangiography (Fig. 2).6 These types include: type 1, in which stenosis is located only in the lower part of the common bile duct; type 2, in which stenosis is diffusely distributed throughout the intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts; type 3, in which stenosis is detected in both the hilar hepatic region and the lower part of the common bile duct; and type 4, in which strictures of the bile duct are detected only in the hilar hepatic region. Cholangiographic findings in type 1 of our classification can often lead to a misdiagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma, those in type 2 as PSC, and those in types 3, 4 as CC. The role of the IDUS is discrimination between types 3, 4 IgG4-SC, and CC (Fig. 2). We considered that it is difficult to distinguish IgG4-SC from CC on the basis of cholangiography alone.18 Endoscopic retrograde pancreatography is necessary to obtain pancreatograms for diagnosis of AIP. Transpapillary IDUS and biopsy can be performed during ERCP in a single session.
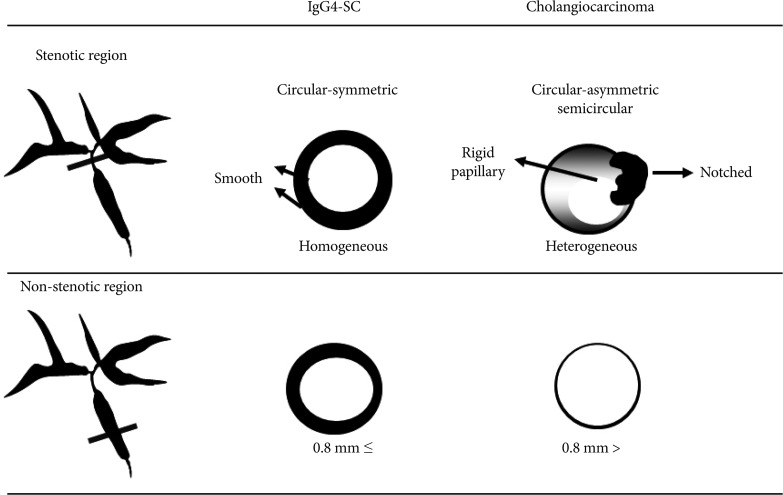
IDUS findings of circular-symmetric wall thickening, a smooth outer margin, a smooth inner margin, a homogeneous internal echo in the stricture were significantly higher in IgG4-SC than in CC (p<0.01) (Fig. 3).10 The most characteristic IDUS finding in the cases of IgG4-SC was wall thickness in the bile duct that had appeared normal in the cholangiogram (Figs. 3, 4). Wall thickness spread continuously from the intrapancreatic bile duct to the upper bile duct in most cases. The wall thickness in IgG4-SC in regions of non-stricture on the cholangiogram was significantly greater than that in CC (p<0.0001). Our previous data showed that the mean wall thickness in areas without stenosis in patients with IgG4-SC was 1.2┬▒0.3 mm, whereas that in CC patients was less than 0.8 mm and mean wall thickness was 0.5┬▒0.1 mm. The best cutoff value of the bile duct wall thickness that had appeared normal in a cholangiogram was 0.8 mm by receiver operating characteristic curves used to differentiate IgG4-SC from CC. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 95%, 90.9%, and 93.5%, respectively, when the cutoff value was 0.8 mm. There were no CC cases in which wall thickness was greater than 1 mm. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 85%, 100%, and 87%, respectively, when the cutoff value was set as 1 mm. We considered 1 mm diameter wall thickness as an optimal cutoff value to completely exclude CC.
The usefulness of endoscopic biliary biopsy for diagnosis of IgG4-associated cholangitis have been reported.19,20 Ghazale et al.19 and Kawakami et al.20 have reported that positive abundant IgG4 immunostaining (10 IgG4-positive cell/high power field) of bile duct biopsy specimens was present in 14 of 16 patients (88%) and 15/29 patients (52%), respectively. However, we were unable to diagnose any cases as IgG4-SC on the basis of H&E and Elastica Van Gieson stain alone.10 Abundant IgG4-positive plasma cells were observed in only three (18%) of 17 patients. We were able to diagnose only three patients (18%) as having IgG4-SC on the basis of its characteristic histopathologic features. However, it was possible to rule out CC by transpapillary biopsy. In addition, one of 11 CC cases showed abundant IgG4-positive plasma cells. Zhang et al.21 also reported that abundant IgG4-positive plasma cells were evident in seven of 38 (18%) cases of non-PSC-related CC. We could exclude CC by transpapillary biopsy. It should be noted that the superficial nature of endoscopic biopsy specimens limits their usefulness for demonstrating the characteristic histology of IgG4-SC.
In summary, the characteristic IDUS features of IgG4-SC are useful for distinction of IgG4-SC from CC. Transpapillary biopsy is not useful for diagnosis of IgG4-SC even when immunohistochemistry is used, but it allows distinction of IgG4-SC from CC. IDUS and transpapillary biopsy after ERCP are useful procedures for the diagnosis of IgG4-SC.
CONCLUSIONS
IDUS provides useful information for the diagnosis of CC and IgG4-SC after ERCP in a single session.
Malignancy is suspected when IDUS shows a hypoechoic mass with irregular margins and inhomogeneous low-echo areas invading the surrounding tissue. It is important to precisely estimate the longitudinal extent of CC preoperatively for curative surgery. CC can be classified into two categories by the type of tumor extension, i.e., intraductal-growth type (superficial spreading) and infiltrating type (submucosal extension). In both types of CC, IDUS is recommended for assessing the longitudinal extent of CC.
It is difficult to discriminate types 3, 4 IgG4-SC from CC on the basis of cholangiographic findings alone. IDUS findings of circular, symmetric wall thickness, a smooth outer margin, a smooth inner margin, and a homogeneous internal echo in the stricture were significantly higher in IgG4-SC than in CC (p<0.01). A bile duct wall thickness exceeding 0.8 mm in regions of non-stricture on the cholangiogram was highly suggestive of IgG4-SC (sensitivity, 95.0%; specificity, 90.9%; accuracy, 93.5%).