AbstractMany advances have been achieved in biliary stenting over the past 30 years. Endoscopic stent placement has become the primary management therapy to relieve obstruction in patients with benign or malignant biliary tract diseases. Compared with plastic stents, a self-expandable metallic stent (SEMS) has been used for management in patients with malignant strictures because of a larger lumen and longer stent patency. Recently, SEMS has been used for various benign biliary strictures and leaks. In this article, we briefly review the characteristics of SEMS as well as complications of stent placement. We review the current guidelines for managing malignant and benign biliary obstructions. Recent developments in biliary stenting are also discussed.
INTRODUCTIONBiliary obstruction can result from various benign and malignant diseases, including primary pancreaticobiliary cancer, metastatic disease, malignant lymphadenopathy, choledocholithiasis, chronic pancreatitis, and postoperative strictures [1]. Hepatobiliary malignancy causes obstruction in 70% to 90% of patients. For patients with malignant biliary obstruction, curative resection is only possible in less than 20% of candidates because of an inoperable condition secondary to local spread and distant metastases [1-6]. In addition, benign biliary strictures can cause jaundice, pain, pruritus, hepatocellular dysfunction, biliary cirrhosis, and cholangitis [3].
Endoscopic biliary stenting was first introduced in the early 1980s [7]. In the late 1980s, the self-expandable metallic stent (SEMS) was introduced and has been shown to improve patency better than plastic stents [8-10]. Since their development, biliary stents have been widely used to manage not only malignant biliary obstruction but also benign biliary diseases. In 2012, the European Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) published clinical guidelines for biliary stenting that included the indications, choice of stents, and results (Table 1) [11,12]. In this article, we review the characteristics of metallic biliary stents and complications of stent placement. We also describe the use of stents in a variety of clinical settings and the technical considerations for stenting. Recent advancements and future directions in biliary stenting including some novel stent designs are also discussed.
SELF-EXPANDING METALLIC STENTMetallic stents are usually made with cobalt-chromium (stainless steel) or an alloy, including nickel-titanium (nitinol), which is a shape memory alloy [13,14]. SEMS, which expands to full diameter once it is placed in the body, is widely used. Because the diameter at full SEMS expansion is 6 to 10 mm, the duration of patency is much longer, approximately 10 months. The stent length is typically 4 to 12 cm; however, some manufacturers will create stents of different lengths to order [13]. A biliary SEMS is released by retracting the sheath from a preloaded, through-the-scope delivery system with a diameter of 6 to 8.5 Fr [7,12]. The primary disadvantage of SEMS is the expense [15].
Stents can be classified as either a closed-cell or open-cell type, depending on the lattice structure. Most stents are the closed-cell type. Depending on the weave of the metallic fibers, these stents can be further classified into cross wire, hook wire, or hook and cross wire structures [15,16]. Most manufacturers use a hook and cross wire structure to take advantage of the positive features of both structures.
A Zilver stent is an open-cell type stent that does not shorten. The delivery system diameter is 7 Fr, and it is easy to access the stenotic lesion in the bile duct. However, its expandability is weaker than other products; the restoring force is high, and it is difficult to reposition the stent when trying to modify the position [15,16].
Ingrowth, in which a tumor grows between the mesh lines of the stent, and overgrowth, in which a tumor blocks either the proximal or distal end of the stent, are primary mechanisms of SEMS occlusion [7,15,16]. To overcome these limitations and prolong the patency duration, a covered SEMS (CSEMS) was developed. The covering materials include polyurethane, silicone, and polytetrafluoroethylene, all of which are effective. An uncovered SEMS (USEMS) is completely buried inside the tumor and helps to prevent migration. It can be placed in the intrahepatic duct [12]. Disadvantages of USEMS are that it is impossible to change or remove once placed and early occlusion can occur due to tumor ingrowth. Although a CSEMS could decrease occlusion, many studies have reported no differences in patency duration between CSEMS and USEMS [11,17-19]. Furthermore, cholecystitis or pancreatitis can occur because the stent covering blocks the opening of cystic or pancreatic ducts, but this is not largely different from a USEMS [18,19]. The frequency of stent migration is much higher with CSEMS than with USEMS (Table 2) [11,20].
EFFICACY AND OUTCOMESBenign biliary diseaseBenign biliary stricturesBenign biliary strictures can result from postoperative biliary injuries (mainly cholecystectomy or liver transplantation), chronic pancreatitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, or other chronic inflammatory disorders [13]. The standard strategy for benign biliary strictures is endoscopic management by placement of multiple plastic stents, with or without balloon dilatation, until resolution of the stricture [21]. According to the ESGE guidelines, temporary simultaneous placement of multiple plastic stents for benign common bile duct (CBD) strictures is technically feasible in more than 90% of patients, and endoscopy provides superior long-term stricture resolution; 90% of postoperative injuries and 65% of strictures are related to chronic pancreatitis [11]. The main limitation of the multi-stenting strategy is that the stent should be exchanged periodically (on average, between 3 to 5 sessions) for more than 1 year for complete resolution of the stricture, which increases costs and may decrease patient compliance [21,22].
Recently, SEMS has become available for various benign biliary strictures. Although USEMS is strongly discouraged in benign biliary strictures, CSEMS, which can be removed using an endoscopic approach, could potentially decrease the number of endoscopic procedures. Technically, it is also easier than insertion of multiple plastic stents [21]. In a recent, large, prospective multinational study, the rates of stricture resolution were 90.5%, 88.0%, and 90.9% for chronic pancreatitis, orthotopic liver transplantation, and cholecystectomy groups, respectively, who underwent scheduled fully CSEMS (FCSEMS)[23]. However, CSEMS can increase the risk of stent migration, and pancreatitis is a well-known complication. Cholecystitis and cholangitis due to obstruction of the cystic duct by the inserted stent are not uncommon adverse events [24]. The potential risk of contralateral biliary occlusion could also be a limitation to the use of CSEMS in hilar strictures [1,21]. Therefore, CSEMS might be a suitable alternative therapeutic option in select conditions only, such as refractory benign biliary stricture or stricture from chronic pancreatitis, especially for calcific pancreatitis, which is difficult to treat, and should not be used routinely [21,25-28]. The respective roles of treatment strategies for benign biliary strictures of various causes are shown in Table 3.
Biliary leaksBile leaks could successfully be treated with plastic stent placement with or without sphincterotomy in 70% to 100% of patients [13,29-32]. A single plastic stent with or without sphincterotomy could be used first in postoperative bile leaks because the CBD is usually not dilated and an insertion of multiple stents or SEMS is difficult. In case of refractory bile leaks, multiple stents or SEMS could be considered. Some studies with small sample sizes have demonstrated complete resolution of large complex leaks and refractory bile leaks with failed plastic stent placements using partially CSEMS or FCSEMS [33-35]. The placement of SEMS may reduce the pressure of the sphincter of Oddi and also seal the fistula [36].
Biliary stonesA previous study reported that biliary stone removal fails 5% to 10% of the time after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) [12]. Biliary stenting can help relieve biliary obstruction by bile drainage and stone dissolution. Short-term plastic stent placement could reduce the size or number of biliary stones and facilitate stone removal in over 90% of cases in subsequent procedures [13,37-39]. Cerefice et al. [40] reported a similar outcome using temporary CSEMS placement for complex biliary stone clearance during initial ERCP after a previous unsuccessful stone extraction.
Bleeding and perforationRecent studies described the use of CSEMS for hemostasis (mainly postsphincterotomy bleeding). CSEMS works by tamponading the bleeding site and provides simultaneous and effective drainage of the bile duct, especially when occluded with blood clots [36,41,42]. Perforations from a guidewire or basket insertion are usually small and can be treated with conservative management. The management of a periampullary perforation remains controversial. Recently, FCSEMS has become a therapeutic option to seal perforations and prevent entry into the perforation site [43,44].
Malignant biliary diseaseDistal malignant biliary obstructionDistal malignant biliary obstruction is usually due to pancreatic cancer, distal cholangiocarcinoma, ampullary cancer, and less commonly gallbladder cancer and metastatic diseases [36]. USEMS, partially CSEMS, and FCSEMS are used for palliation of patients with a distal malignant biliary obstruction.
In patients with a prognosis of less than 4 months, plastic stents are a better choice because they are cost-effective and the risk of both migration and occlusion within approximately 3 months is low [12,45]. If expected survival is more than 4 months; however, a recent meta-analysis reported that, compared with a plastic stent, SEMS in the management of malignant biliary obstruction is associated with significantly longer stent patency, fewer ERCPs, and longer patient survival [36,46]. A meta-analysis showed no differences between CSEMS and USEMS in the patency rates at 6 or 12 months. There was also no difference in pancreatitis, cholecystitis, perforation, bleeding, cholangitis, length of hospital stay, or number of recurrent biliary obstructions [47]. However, CSEMS is associated with a higher rate of stent migration than USEMS [47]. In a multicenter, randomized controlled trial with 400 patients, there was no significant difference in stent patency between USEMS and CSEMS for distal malignant biliary disease [18].
All of these studies support the guidelines issued by the ESGE in 2012 for nonresectable malignant biliary obstruction and show that plastic stents are a good option when patient prognosis is less than 4 months, while SEMS is a better option if the prognosis is more than 4 months (Table 1) [11,12]. The guidelines do not identify a benefit for CSEMS over USEMS in the treatment of nonhilar biliary obstructions [11,12], and the best choice remains controversial.
Hilar malignant biliary obstructionHilar obstruction can be caused by primary tumors such as cholangiocarcinoma (Klatskin tumor), local extension from gallbladder carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, and metastatic diseases or compression from lymph nodes. Tumor resectability should be evaluated using imaging techniques before biliary stenting in malignant hilar obstruction [11]. The benefit of preoperative drainage in malignant hilar obstruction is less clear.
A meta-analysis of 11 studies reported no difference in mortality or length of postoperative stay with and without preoperative biliary drainage in jaundiced patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma, as well as increased overall rates of postoperative and infectious complications [48,49]. Therefore, preoperative biliary drainage should not be routinely performed. However, in Korea and Japan, biliary drainage via a percutaneous approach is preferred for patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma [50-52]. Preoperative biliary drainage can be a reasonable choice under certain conditions such as right lobectomy for Bismuth type IIIA or IV hilar cholangiocarcinoma or preoperative portal vein embolization with chemoradiation therapy [53].
Endoscopic palliation, combined percutaneous and endoscopic procedures (especially after a failed endoscopic procedure), or percutaneous drainage alone have been used for unresectable malignant hilar tumors [54]. In general, endoscopic management is the preferred treatment for palliation. Previous studies suggest that SEMS is superior to plastic stents for the treatment of hilar malignancy [55-58]. The placement of SEMS is especially recommended for patients with expected survival more than 3 months or with infected bile duct. CSEMS is not appropriate for palliative drainage of hilar malignant obstruction because it occludes the contralateral biliary duct and has migration issues [12]. Although the use of unilateral or bilateral stents is debated, the important step is draining more than 50% of the liver volume, which reportedly results in a greater decrease in bilirubin level, lower incidence of early cholangitis, and longer patient survival [59].
Bismuth classification is useful for endoscopic stent placement planning. In patients with Bismuth type I cholangiocarcinoma, only one stent in the common duct is appropriate for drainage. Palliation of the other lesion types, especially types III and IV, risks incomplete drainage and requires multiple stents [36,52,60]. Additionally, contrast injection into an undrained biliary system can lead to a higher rate of post-procedure cholangitis and decrease the survival rate [61]. Prophylactic antibiotics are needed routinely. Bilateral stent insertion preserves the functional liver volume, decreases the potential risk of cholangitis, and lowers complications when there are bilateral infected ducts, extending patient survival [60]. The Asia-Pacific Consensus developed an algorithm for palliative biliary drainage in hilar cholangiocarcinoma (Fig. 1) [52]. However, an endoscopic approach may be considered as the initial strategy in actual clinical practice at many centers.
Bilateral stenting is difficult and technically challenging. Bilateral biliary drainage with SEMS can be performed using two methods, the ŌĆ£side-by-sideŌĆØ and ŌĆ£stent in-stentŌĆØ (also called ŌĆ£through-the-meshŌĆØ) methods. The technical success rates are 73.3% and 100%, and the functional success rates are 75% and 100%, respectively [62]. Although the stent in-stent method seems to be theoretically more physiological due to suitable bile duct configuration, the selection of side-by-side versus stent-in-stent placement for hilar biliary obstruction is still controversial. In a recent study, the side-by-side method resulted in a higher incidence of complications, but tended to be superior in cumulative stent patency [63]. Newly designed SEMS such as the Y-configured stent (Y type biliary Niti-S stent; Taewoong Inc., Seoul, Korea and M-Hilar and K-Hilar stents; Standard Sci-Tech Inc., Seoul, Korea) have a relatively high success rate for hilar biliary strictures [64-66]. Modifying the stents and improvement of the skill or technique in the stent-in-stent method are expected to lead to wider use of these stents. Additionally, minor (limited) endoscopic sphincterotomy may be a better strategy to achieve successful stent placement requiring complex procedural techniques. Further high-quality comparative studies are needed to determine the best therapy using these stent types and procedures.
NOVEL STENTSBoth plastic stents and SEMS are continuously undergoing functional enhancements. Additionally, a variety of functional stents including antimigratory stents, antireflux stents, drug-eluting stents, radioactive stents, and bioabsorbable stents are currently under development to overcome the limitations of existing stents.
With FCSEMS, migration is a major problem. Several newly designed stents prevent stent migration; anchoring flaps or flared stent ends are commonly used [67,68]. Studies using FCSEMS with either an anchoring flap or a flared end at the proximal end of the stent reported that the anchoring flap design might be superior in terms of efficacy and a lower migration rate to the flared end [69,70].
Transpapillary SEMS placement may induce duodeno-biliary reflux and lead to cholangitis. FCSEMS with antireflux valves attached at the distal ends is being developed to prevent reflux. Although the results are not always positive due to malfunction of the attached valve, antireflux stents are worthy of further investigation [71]. Regarding malignant biliary obstruction, drug-eluting stents coated with an antitumor agent that inhibits tumor ingrowth may improve stent patency [14]. However, previous studies using paclitaxel-eluting CSEMS have not yet shown a definite advantage in stent patency and patient survival [72]. Additional studies are currently being performed to investigate the appropriate drug concentration and stent membrane type and shape [73-75]. Bioabsorbable stents theoretically may not require stent removal and can be combined with antibacterial or antitumor materials [68,76]. They might be particularly useful for benign biliary strictures and bile duct leaks, but require additional studies and outcome data.
CONCLUSIONSBiliary stents have been used in various malignant and benign biliary obstructions. SEMS has been traditionally used for inoperable malignant biliary obstructions. Regardless of the number of stents deployed, drainage of more than 50% of the liver volume is important for longer patient survival, and endoscopic bilateral metallic stenting could be the preferred treatment for hilar malignant biliary strictures with high-grade obstruction. Although guidelines are lacking, FCSEMS has been proposed as a reasonable alternative therapeutic option for benign biliary disease. Currently, various types of SEMS such as antimigratory, antireflux, drug-eluting, radioactive, and bioabsorbable stents are being studied. Many studies are at a stage of early investigation or in early clinical experiments. However, a customized functional stent appropriate to the disease characteristics of the patient and various other situations should be considered in the future.
Fig.┬Ā1.Palliative biliary drainage in hilar cholangiocarcinoma Bismuth II to IV. Adapted from Rerknimitr et al., with permission from John Wiley and Sons [52]. a)Endoscopic approach may be considered as the initial strategy in actual clinical practice at many centers. 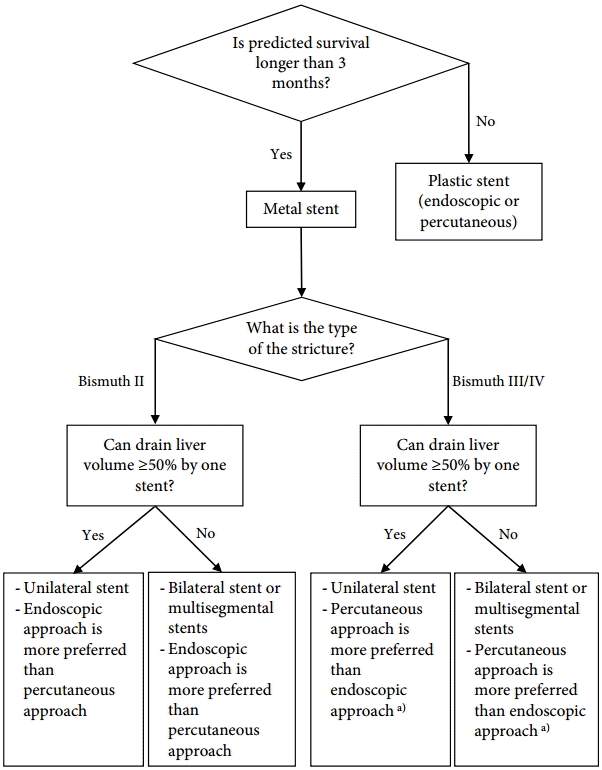
Table┬Ā1.Sphincterotomy is not necessary for inserting a single plastic stent or a SEMS, but may facilitate more complex procedures. Adapted from Moy et al. [12]. CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; SEMS, self-expanding metal stent; ERCP, esophageal retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Table┬Ā2.Stent-Related Complication [11] Table┬Ā3.Main Causes of Benign Biliary Strictures and the Respective Role of Endoscopic Treatment [14] REFERENCES1. Hair CD, Sejpal DV. Future developments in biliary stenting. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 2013;6:91ŌĆō99.
2. Levy MJ, Baron TH, Gostout CJ, Petersen BT, Farnell MB. Palliation of malignant extrahepatic biliary obstruction with plastic versus expandable metal stents: an evidence-based approach. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;2:273ŌĆō285.
3. Geer RJ, Brennan MF. Prognostic indicators for survival after resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg 1993;165:68ŌĆō72.
4. Guthrie CM, Haddock G, De Beaux AC, Garden OJ, Carter DC. Changing trends in the management of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Surg 1993;80:1434ŌĆō1439.
5. Smith AC, Dowsett JF, Russell RC, Hatfield AR, Cotton PB. Randomised trial of endoscopic stenting versus surgical bypass in malignant low bileduct obstruction. Lancet 1994;344:1655ŌĆō1660.
6. Prat F, Chapat O, Ducot B, et al. Predictive factors for survival of patients with inoperable malignant distal biliary strictures: a practical management guideline. Gut 1998;42:76ŌĆō80.
8. Huibregtse K, Cheng J, Coene PP, Fockens P, Tytgat GN. Endoscopic placement of expandable metal stents for biliary strictures: a preliminary report on experience with 33 patients. Endoscopy 1989;21:280ŌĆō282.
9. Neuhaus H, Hagenmuller F, Classen M. Self-expanding biliary stents: preliminary clinical experience. Endoscopy 1989;21:225ŌĆō228.
10. Irving JD, Adam A, Dick R, Dondelinger RF, Lunderquist A, Roche A. Gianturco expandable metallic biliary stents: results of a European clinical trial. Radiology 1989;172:321ŌĆō326.
11. Dumonceau JM, Tringali A, Blero D, et al. Biliary stenting: indications, choice of stents and results. European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) clinical guideline. Endoscopy 2012;44:277ŌĆō298.
13. ASGE Technology Assessment Committee, Pfau PR, Pleskow DK, et al. Pancreatic and biliary stents. Gastrointest Endosc 2013;77:319ŌĆō327.
14. Chun HJ, Kim ES, Hyun JJ, Kwon YD, Keum B, Kim CD. Gastrointestinal and biliary stents. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;25:234ŌĆō243.
15. Jeong S, Lee DH. Review of current metal stent. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 2010;40(Suppl 1):348ŌĆō353.
16. Kwon CI, Jeong S. Choice of stents for distal biliary obstruction. Clin Endosc 2013;46(Suppl):295ŌĆō302.
17. Isayama H, Komatsu Y, Tsujino T, et al. A prospective randomised study of ŌĆ£coveredŌĆØ versus ŌĆ£uncoveredŌĆØ diamond stents for the management of distal malignant biliary obstruction. Gut 2004;53:729ŌĆō734.
18. Kullman E, Frozanpor F, Soderlund C, et al. Covered versus uncovered self-expandable nitinol stents in the palliative treatment of malignant distal biliary obstruction: results from a randomized, multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 2010;72:915ŌĆō923.
19. Telford JJ, Carr-Locke DL, Baron TH, et al. A randomized trial comparing uncovered and partially covered self-expandable metal stents in the palliation of distal malignant biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc 2010;72:907ŌĆō914.
20. Suk KT, Kim HS, Kim JW, et al. Risk factors for cholecystitis after metal stent placement in malignant biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc 2006;64:522ŌĆō529.
21. Pausawasadi N, Soontornmanokul T, Rerknimitr R. Role of fully covered self-expandable metal stent for treatment of benign biliary strictures and bile leaks. Korean J Radiol 2012;13 Suppl 1:S67ŌĆōS73.
22. Costamagna G, Boskoski I. Current treatment of benign biliary strictures. Ann Gastroenterol 2013;26:37ŌĆō40.
23. Deviere J, Nageshwar Reddy D, Puspok A, et al. Successful management of benign biliary strictures with fully covered self-expanding metal stents. Gastroenterology 2014;147:385ŌĆō395.
24. Ho H, Mahajan A, Gosain S, et al. Management of complications associated with partially covered biliary metal stents. Dig Dis Sci 2010;55:516ŌĆō522.
25. Mahajan A, Ho H, Sauer B, et al. Temporary placement of fully covered self-expandable metal stents in benign biliary strictures: midterm evaluation (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2009;70:303ŌĆō309.
26. Behm B, Brock A, Clarke BW, et al. Partially covered self-expandable metallic stents for benign biliary strictures due to chronic pancreatitis. Endoscopy 2009;41:547ŌĆō551.
27. Traina M, Tarantino I, Barresi L, et al. Efficacy and safety of fully covered self-expandable metallic stents in biliary complications after liver transplantation: a preliminary study. Liver Transpl 2009;15:1493ŌĆō1498.
28. Garcia-Pajares F, Sanchez-Antolin G, Pelayo SL, et al. Covered metal stents for the treatment of biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 2010;42:2966ŌĆō2969.
29. Bridges A, Wilcox CM, Varadarajulu S. Endoscopic management of traumatic bile leaks. Gastrointest Endosc 2007;65:1081ŌĆō1085.
30. Sandha GS, Bourke MJ, Haber GB, Kortan PP. Endoscopic therapy for bile leak based on a new classification: results in 207 patients. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;60:567ŌĆō574.
31. Bhattacharjya S, Puleston J, Davidson BR, Dooley JS. Outcome of early endoscopic biliary drainage in the management of bile leaks after hepatic resection. Gastrointest Endosc 2003;57:526ŌĆō530.
32. Kaffes AJ, Hourigan L, De Luca N, Byth K, Williams SJ, Bourke MJ. Impact of endoscopic intervention in 100 patients with suspected postcholecystectomy bile leak. Gastrointest Endosc 2005;61:269ŌĆō275.
33. Wang AY, Ellen K, Berg CL, Schmitt TM, Kahaleh M. Fully covered self-expandable metallic stents in the management of complex biliary leaks: preliminary data. A case series. Endoscopy 2009;41:781ŌĆō786.
34. Kahaleh M, Behm B, Clarke BW, et al. Temporary placement of covered self-expandable metal stents in benign biliary strictures: a new paradigm? (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2008;67:446ŌĆō454.
35. Baron TH, Poterucha JJ. Insertion and removal of covered expandable metal stents for closure of complex biliary leaks. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;4:381ŌĆō386.
36. Mangiavillano B, Pagano N, Baron TH, Luigiano C. Outcome of stenting in biliary and pancreatic benign and malignant diseases: a comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:9038ŌĆō9054.
37. Hong WD, Zhu QH, Huang QK. Endoscopic sphincterotomy plus endoprostheses in the treatment of large or multiple common bile duct stones. Dig Endosc 2011;23:240ŌĆō243.
38. Horiuchi A, Nakayama Y, Kajiyama M, et al. Biliary stenting in the management of large or multiple common bile duct stones. Gastrointest Endosc 2010;71:1200ŌĆō1203.
39. Han J, Moon JH, Koo HC, et al. Effect of biliary stenting combined with ursodeoxycholic acid and terpene treatment on retained common bile duct stones in elderly patients: a multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:2418ŌĆō2421.
40. Cerefice M, Sauer B, Javaid M, et al. Complex biliary stones: treatment with removable self-expandable metal stents: a new approach (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 2011;74:520ŌĆō526.
41. Canena J, Liberato M, Horta D, Romao C, Coutinho A. Short-term stenting using fully covered self-expandable metal stents for treatment of refractory biliary leaks, postsphincterotomy bleeding, and perforations. Surg Endosc 2013;27:313ŌĆō324.
42. Irani S, Baron TH, Law R, et al. Endoscopic treatment of nonstricture-related benign biliary diseases using covered self-expandable metal stents. Endoscopy 2015;47:315ŌĆō321.
43. Lee SM, Cho KB. Value of temporary stents for the management of perivaterian perforation during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. World J Clin Cases 2014;2:689ŌĆō697.
44. Abdel Samie A, Theilmann L. Fully covered self-expandable metal stents for treatment of both benign and malignant biliary disorders. Diagn Ther Endosc 2012;2012:498617.
45. Soderlund C, Linder S. Covered metal versus plastic stents for malignant common bile duct stenosis: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2006;63:986ŌĆō995.
46. Hong WD, Chen XW, Wu WZ, Zhu QH, Chen XR. Metal versus plastic stents for malignant biliary obstruction: an update meta-analysis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 2013;37:496ŌĆō500.
47. Almadi MA, Barkun AN, Martel M. No benefit of covered vs uncovered self-expandable metal stents in patients with malignant distal biliary obstruction: a meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;11:27ŌĆō37.
48. Hochwald SN, Burke EC, Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, Blumgart LH. Association of preoperative biliary stenting with increased postoperative infectious complications in proximal cholangiocarcinoma. Arch Surg 1999;134:261ŌĆō266.
49. Liu F, Li Y, Wei Y, Li B. Preoperative biliary drainage before resection for hilar cholangiocarcinoma: whether or not? A systematic review. Dig Dis Sci 2011;56:663ŌĆō672.
50. Nimura Y. Preoperative biliary drainage before resection for cholangiocarcinoma (Pro). HPB (Oxford) 2008;10:130ŌĆō133.
51. Lee SG, Song GW, Hwang S, et al. Surgical treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma in the new era: the Asan experience. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2010;17:476ŌĆō489.
52. Rerknimitr R, Angsuwatcharakon P, Ratanachu-ek T, et al. Asia-Pacific consensus recommendations for endoscopic and interventional management of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;28:593ŌĆō607.
53. Paik WH, Loganathan N, Hwang JH. Preoperative biliary drainage in hilar cholangiocarcinoma: when and how? World J Gastrointest Endosc 2014;6:68ŌĆō73.
54. Kim JH. Endoscopic stent placement in the palliation of malignant biliary obstruction. Clin Endosc 2011;44:76ŌĆō86.
55. Perdue DG, Freeman ML, DiSario JA, et al. Plastic versus self-expanding metallic stents for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a prospective multicenter observational cohort study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2008;42:1040ŌĆō1046.
56. Peters RA, Williams SG, Lombard M, Karani J, Westaby D. The management of high-grade hilar strictures by endoscopic insertion of self-expanding metal endoprostheses. Endoscopy 1997;29:10ŌĆō16.
57. Wagner HJ, Knyrim K, Vakil N, Klose KJ. Plastic endoprostheses versus metal stents in the palliative treatment of malignant hilar biliary obstruction. A prospective and randomized trial. Endoscopy 1993;25:213ŌĆō218.
58. Sangchan A, Kongkasame W, Pugkhem A, Jenwitheesuk K, Mairiang P. Efficacy of metal and plastic stents in unresectable complex hilar cholangiocarcinoma: a randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2012;76:93ŌĆō99.
59. Vienne A, Hobeika E, Gouya H, et al. Prediction of drainage effectiveness during endoscopic stenting of malignant hilar strictures: the role of liver volume assessment. Gastrointest Endosc 2010;72:728ŌĆō735.
60. Jang SI, Lee DK. Update on pancreatobiliary stents: stent placement in advanced hilar tumors. Clin Endosc 2015;48:201ŌĆō208.
61. Ertugrul I, Yuksel I, Parlak E, et al. Risk factors for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography-related cholangitis: a prospective study. Turk J Gastroenterol 2009;20:116ŌĆō121.
62. Lee TH, Moon JH, Park SH. Bilateral metallic stenting in malignant hilar obstruction. Clin Endosc 2014;47:440ŌĆō446.
63. Naitoh I, Hayashi K, Nakazawa T, et al. Side-by-side versus stent-in-stent deployment in bilateral endoscopic metal stenting for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Dis Sci 2012;57:3279ŌĆō3285.
64. Lee JH, Kang DH, Kim JY, et al. Endoscopic bilateral metal stent placement for advanced hilar cholangiocarcinoma: a pilot study of a newly designed Y stent. Gastrointest Endosc 2007;66:364ŌĆō369.
65. Hwang JC, Kim JH, Lim SG, Kim SS, Yoo BM, Cho SW. Y-shaped endoscopic bilateral metal stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: prospective long-term study. Scand J Gastroenterol 2011;46:326ŌĆō332.
66. Park do H, Lee SS, Moon JH, et al. Newly designed stent for endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent placement of metallic stents in patients with malignant hilar biliary strictures: multicenter prospective feasibility study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 2009;69:1357ŌĆō1360.
67. Park JS, Jeong S, Lee DH. Recent advances in gastrointestinal stent development. Clin Endosc 2015;48:209ŌĆō215.
68. Kwon CI, Ko KH, Hahm KB, Kang DH. Functional self-expandable metal stents in biliary obstruction. Clin Endosc 2013;46:515ŌĆō521.
69. Tringali A, Familiari P, Mutignani M, Perri V, Costamagna G. Self-expandable, removable, fully covered metal stents to dilate common bile duct strictures secondary to chronic pancreratitis: preliminary results. Gastrointest Endosc 2010;71:AB169ŌĆōAB170.
70. Park do H, Lee SS, Lee TH, et al. Anchoring flap versus flared end, fully covered self-expandable metal stents to prevent migration in patients with benign biliary strictures: a multicenter, prospective, comparative pilot study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 2011;73:64ŌĆō70.
71. Kim DU, Kwon CI, Kang DH, Ko KH, Hong SP. New antireflux self-expandable metal stent for malignant lower biliary obstruction: in vitro and in vivo preliminary study. Dig Endosc 2013;25:60ŌĆō66.
72. Song TJ, Lee SS, Yun SC, et al. Paclitaxel-eluting covered metal stents versus covered metal stents for distal malignant biliary obstruction: a prospective comparative pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc 2011;73:727ŌĆō733.
73. Jang SI, Kim JH, Kim M, et al. Porcine feasibility and safety study of a new paclitaxel-eluting biliary stent with a Pluronic-containing membrane. Endoscopy 2012;44:825ŌĆō831.
74. Chung MJ, Kim H, Kim KS, Park S, Chung JB, Park SW. Safety evaluation of self-expanding metallic biliary stents eluting gemcitabine in a porcine model. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;27:261ŌĆō267.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
