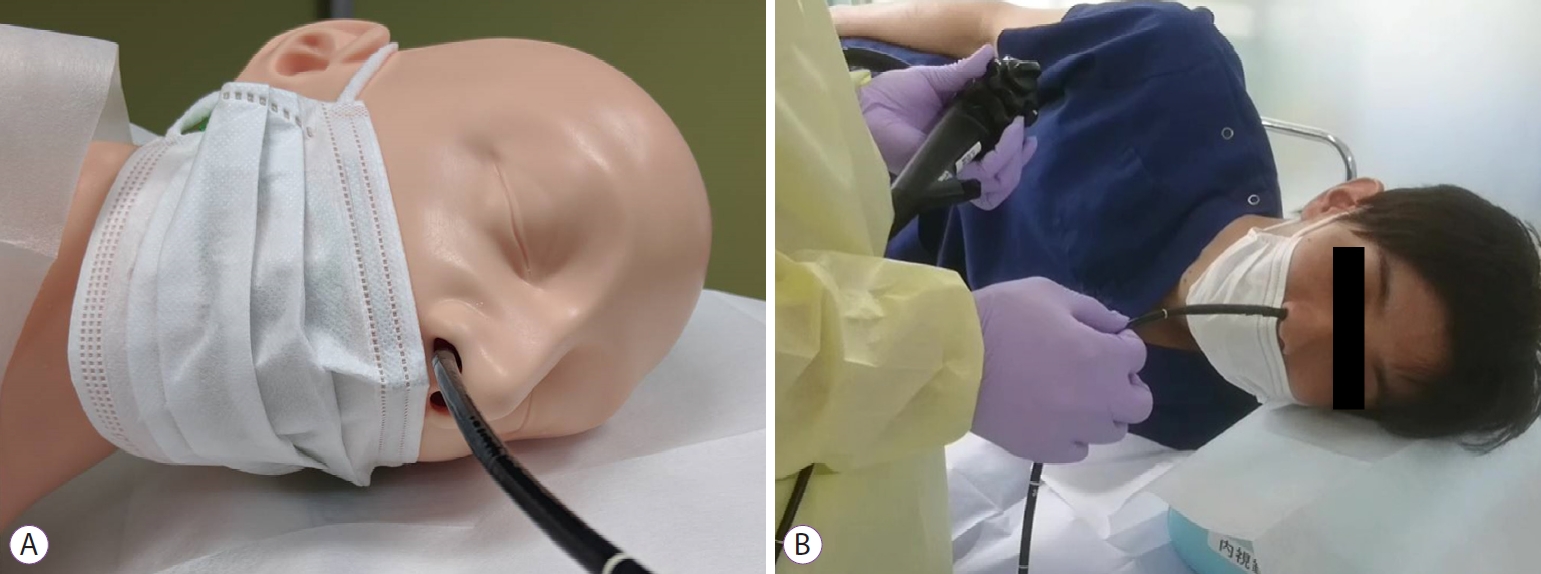
The Coronavirus-19 (COVID-19) pandemic continues to accelerate worldwide [1]. Since endoscopy may pose a risk for transmission, there is a medical need to establish a ŌĆ£new normalŌĆØ for endoscopic procedures that reduce the risk. Although we previously reported a technique to prevent infection during endoscopy, it did not completely block leakage of aerosol droplets through the hole in a modified mask [2]. Hence, we propose a safer method using a transnasal endoscope (Fig. 1). Transnasal endoscopy is widely used in screening for upper gastrointestinal lesions, especially in health check-up centers in Japan.
In our simulation (Supplementary Video 1), transnasal endoscopy was performed on a mannequin with and without a surgical mask (PRO-LINE, American Society of Testing and Materials Level 1 mask; A.R. Medicom Inc., Ltd., Kobe, Japan), using an ultrathin endoscope (GIF-XP290N; Olympus Medical System, Tokyo, Japan). Coughs were simulated using a 0.4 MPa pressure accumulation sprayer containing 10 mL of fluorescent dye [3-5], and the spread of the scattered dye droplets was visualized under ultraviolet light.
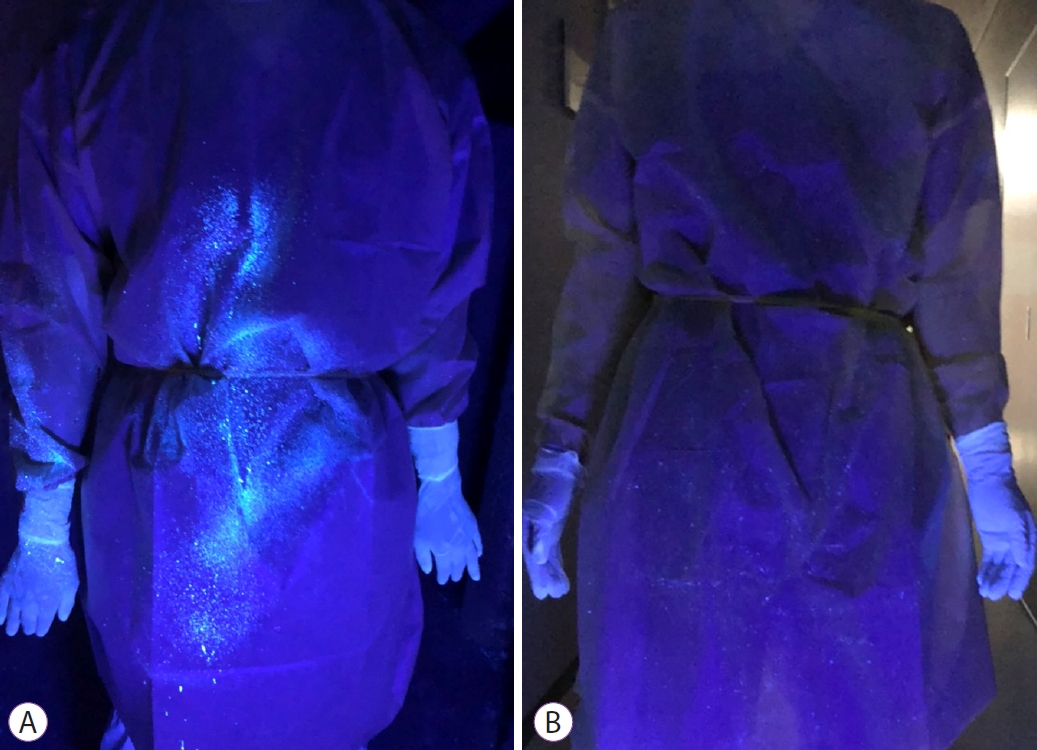
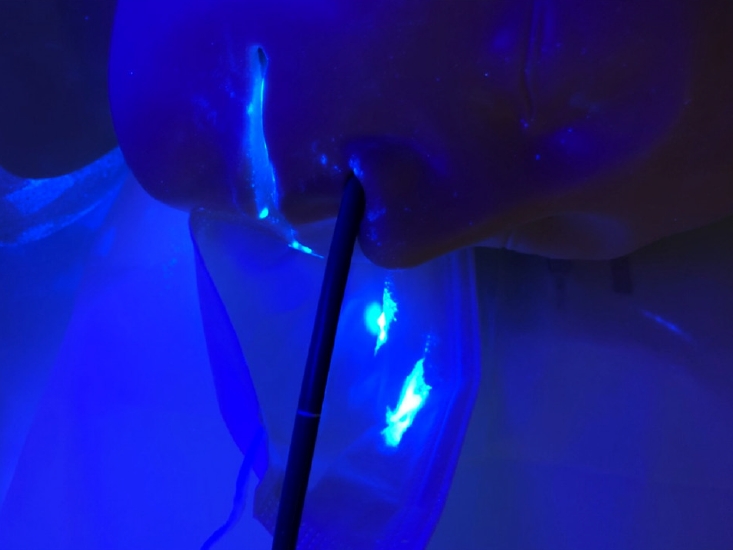
Following the procedure performed without a surgical mask, the dye was found on the endoscopistŌĆÖs gloves, upper chest, abdomen, and shoe covers (Fig. 2A), and floor contamination of up to approximately 1.5 m away from the bed was observed. When transnasal endoscopy was performed with a surgical mask, the simulated cough contaminated only the inner surface of the mask (Fig. 3), with no detectable dye deposits on the endoscopist (Fig. 2B) or the floor. For clinical validation, 732 patients underwent screening transnasal endoscopy while wearing a mask. During those procedures, vital signs were unaffected and no problems were encountered.
This new and safer method completely covered the examineeŌĆÖs mouth with a surgical mask and prevented the spread of aerosol droplets. Transnasal endoscopy is well tolerated, and is also a valuable diagnostic tool. Furthermore, transnasal endoscopy can reduce pharyngeal stimulation, resulting in less coughing and reduction of the vomiting reflex than occurs during per-oral endoscopy. Therefore, we propose the adoption of this method as the ŌĆ£new normalŌĆØ for endoscopy following the COVID-19 pandemic.