AbstractSedation can resolve anxiety and fear in patients undergoing endoscopy. The use of sedatives has increased in Korea. Appropriate sedation is a state in which the patient feels subjectively comfortable while maintaining the airway reflex for stable spontaneous breathing. The patient should maintain a state of consciousness to the extent that he or she can cooperate with the needs of the medical staff. Despite its benefits, endoscopic sedation has been associated with cardiopulmonary complications. Cardiopulmonary complications are usually temporary. Most patients recover without sequelae. However, they may progress to serious complications, such as cardiovascular collapse. Therefore, it is essential to screen high-risk patients before sedation and reduce complications by meticulous monitoring. Additionally, physicians should be familiar with the management of emergencies. The first Korean clinical practice guideline for endoscopic sedation was developed based on previous worldwide guidelines for endoscopic sedation using an adaptation process. The guideline consists of nine recommendations based on a critical review of currently available data and expert consensus when the guideline was drafted. These guidelines should provide clinicians, nurses, medical school students, and policy makers with information on how to perform endoscopic sedation with minimal risk.
INTRODUCTIONBackgroundEndoscopic sedation is performed to reduce the patientŌĆÖs anxiety during the procedure. Due to the high satisfaction with sedation among both endoscopists and patients, the use of endoscopic sedation is on the rise. Although most sedation cases are performed without safety issues, the use of sedatives can result in adverse events (AEs) in some cases. Therefore, clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) for endoscopic sedation, delineating measures for early detection of potential AEs of sedation and prevention of AEs before they progress to fatal stages are needed through active monitoring and emergency response. As each country has unique healthcare settings, CPGs for endoscopic sedation tailored to each country have been published. However, there are no CPGs for endoscopic sedation in Korea so far. Amid the dire need for CPGs tailored to the Korean society, the Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (KSGE) has collaborated with other relevant academic societies to develop multidisciplinary CPGs.
Target population, scope, purpose, and users of clinical practice guidelinesThe present CPGs target all adult males and females who undergo endoscopic sedation. These guidelines contain essential information to evaluate patients and prepare for sedation before endoscopic sedation, monitor patients and oxygenation during sedation, and prepare for discharge after sedation to avoid potential cardiopulmonary complications. In particular, these guidelines focus primarily on moderate sedation, the most widely used type of sedation for endoscopy. The scope of these CPGs was determined by the CPG development group by identifying key questions following the Patient Intervention Comparison Outcomes strategy. The users of these CPGs are all physicians who practice endoscopy and their assistant nursing staff when performing an endoscopic sedation procedure in clinical practice. Furthermore, these guidelines can also be used by medical students, nursing students, residents, and fellows who are in training, and nurses for educational purposes. These guidelines can also be used as a reference for the quality assessment of endoscopy units.
Composition of the clinical practice guidelines committee and multidisciplinary involvementThe committee for the development of this CPGs comprised a Steering Committee (consisting of board members of the KSGE) and a Development Committee (consisting of members of the Endoscopic Sedation Committee of the KSGE, methodology specialists for guidelines, and advisory members from other relevant academic societies). The Steering Committee established strategies and directions for guideline development, appointed a chairperson of the committee, and reviewed and approved the budget. The Steering Committee also mediated between stakeholders regarding guideline development and supervised to ensure independence in editing. The Development Committee was headed by the director of the Endoscopic Sedation Committee of KSGE (Byung-Wook Kim). The assistant administrator (Hong Jun Park) and members of the Endoscopic Sedation Committee of KSGE (Jun Kyu Lee, Yehyun Park, Jin Myung Park, JunYong Bae, Seung Young Seo, Jae Min Lee, Jee Hyun Lee, Hyung Ku Chon, Jun-Won Chung, and Hyun Ho Choi) authored the manuscript for each key question. It has been decided that these CPGs will be developed by adapting existing guidelines. Therefore, a researcher from the National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency (NECA; Dong Ah Park) and an expert from the Center of Evidence Based Medicine Institute of Convergence Science, Yonsei University (Jae Hung Jung), were recruited. A librarian from the medical library at Yonsei University School of Medicine at Wonju (Myung Ha Kim) was also recruited to assist in the literature search. Since 2019, a total of nine rounds of workshops for CPGs for endoscopic sedation were held with board members of the Korea Medical Association, the Korean Society of Anesthesiologists, the Korean Society of Gastroenterology, the Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Nurses and Associates, Korean College of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research, Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases, and Korean Pancreatobiliary Association participating as advisors. The Development Committee evaluated the process with the assistance of a methodology expert. A consensus was reached on the finalized key questions among representatives of the organizations that participated in the development of the CPGs. A conference call was held with the experts.
Internal review, external review, and advice on the draft clinical practice guidelinesRecommendations were first drafted by the Development Committee and reviewed internally. The statements were then sent to each participating organization by e-mail to obtain consent. At the 64th KSGE seminar on August 22, 2021, an online conference call was held with about 300 members to reach a consensus among experts. Feedback was presented during the review process and matters decided by vote were collated to be reviewed and revised. For objective verification, the CPGs were reviewed by two gastroenterologists (Jeong-Sik Byeon, Ulsan University College of Medicine and Hye-Kyung Jung, Ewha WomanŌĆÖs University) who did not participate in CPG development. These CPGs were then discussed and revised by the Development Committee after peer review.
Clinical practice guidelines publication and disseminationCPGs will be available through the KSGE (http://www.gie.or.kr) and the Korean Association of Internal Medicine (KAIM) websites (http://www.kaim.or.kr). The Korean version will be published in the Korean Journal of Gastroenterology, and the English version will be published through Clinical Endoscopy, an official journal of KSGE, along with Gut and Liver, an international journal. In addition, the draft CPGs will be published in A Guidebook on Endoscopic Sedation 2021 revised edition.
Update of clinical practice guidelinesThese CPGs are planned to be updated every 5 years after completion if clinical evidence for safer endoscopic sedation is accumulated or if it is deemed necessary to add a new statement and revise and supplement an existing statement. KSGE primarily undertakes the update process. These CPGs were developed in reference to CPGs published in or before May 2021 and in reference to each item in or before September 2019.
Conflict of interest in guideline developersBefore beginning guideline development, all members were required to sign a document declaring no conflict of interest (COI), such as advising or being employed by a commercially linked organization during the CPG development or approval process, owning commercial shares or receiving research funds or compensation from such organizations, owning intellectual property rights for drugs specified in the guideline development (e.g., patent, trademark rights, licensing, royalty), and having a family member or family memberŌĆÖs affiliation with the above-described relationship. All members declared no COI.
METHOD OF DEVELOPING CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR ENDOSCOPIC SEDATIONRecently published international CPGs for sedation are well organized. They also contain similar content. Therefore, an adaptation method was used to develop CPGs for endoscopic sedation relevant to the Korean environment.
Identification of key questionsThe members of the Development Committee began to identify key questions for endoscopic sedation through nine workshops since 2019. Twenty-two key questions (10 items for pre-sedation, 8 items for intra-sedation, and 4 items for post-sedation) were initially developed. These questions were further reviewed and discussed for redundancy, a reflection of the endoscopic sedation environment in Korea, and effective prevention of fatal AEs. As a result, a total of 10 items (4 items for pre-sedation, 4 items for intra-sedation, and 2 items for post-sedation) were selected. These initially proposed 22 key questions are delineated in Supplementary Table 1, and the selected 10 items are delineated in Supplementary Table 2.
Literature search and quality appraisalThe international CPGs that would serve as the foundation of the Korean CPGs were searched by a librarian in the medical library of Yonsei University School of Medicine in Wonju, Korea. A literature search was conducted in Ovid-MEDLINE, EMBASE, KoreaMed, and KMBASE using the MeSH terms ŌĆ£sedationŌĆØ and ŌĆ£guideline,ŌĆØ with the end date set for September 2019. Searches were also conducted on the CPGs websites, namely the Guidelines International Network, National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE), World Health Organization (WHO), and Korea Medical Citation Index (KoMCI). In total, 946 articles were identified. The following criteria were used for literature selection: (1) evidence-based CPGs; (2) national or international CPGs; (3) (latest) CPGs published in 2010 or later; (4) externally reviewed CPGs; (5) CPGs published in English or Korean; and (6) CPGs published in adjacent countries. CPGs written by a single author that lacked representativeness and CPGs published without reference were excluded (Supplementary Table 3, Fig. 1). The initially selected guidelines included the 2010 European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) CPGs, 2014 Spanish Society of Digestive Endoscopy CPGs, 2015 ESGE CPGs-updated, 2015 Japanese Gastroenterological Endoscopy Society (JGES) CPGs, and American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) 2018 CPGs. An updated version of the 2010 ESGE CPGs was published in 2015. Therefore, the latest version was chosen for these Korean CPGs. The 2014 Spanish Society of Digestive Endoscopy CPGs was excluded due to the lack of an English version. During the development of the Korean CPGs, an update of the JGES CPGs was published in 2020. Thus, the 2020 version was chosen for the JGES CPGs. These selected international CPGs were assessed by four members using the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation (AGREE) 2.0 tool. Three CPGs (2015 ESGE CPGs, 2018 ASGE CPGs, and 2020 JGES CPGs) with an average score of 50% or higher were selected. During the development period, the revised JGES CPGs were published in 2020, and this revised version was assessed using the same method. The revised 2020 version of the JGES CPGs was selected instead of the 2015 version of the JGES CPGs.
Assessment of recencyThe ESGE guidelines, ASGE guidelines, and JGES guidelines included references published up to February 2015, August 2017, and June 2019, respectively. Thus, a recency assessment was performed to add the latest references up to May 2020 for each key question.
Determination of the level of evidence and grade of recommendationIn general, the recommendation grade is commensurate with the level of evidence. However, in the absence of relevant literature, expert opinions were added to the level of evidence. A relatively high grade of recommendation was assigned to practices with weakly supported evidence if the practice was highly useful in clinical practice. Table 1 presents the level of evidence. Table 2 shows the grades of recommendations determined through several rounds of discussion.
Expert consensus and external reviewAfter finalizing the draft, a conference call was held with about 300 experts at the 64th KSGE seminar on August 22, 2021. A five-point rating scale composed of ŌĆ£strongly agree,ŌĆØ ŌĆ£agree,ŌĆØ ŌĆ£neither,ŌĆØ ŌĆ£disagree,ŌĆØ and ŌĆ£strongly disagreeŌĆØ was used, and the consensus was considered reached when ŌĆ£strongly agreeŌĆØ and ŌĆ£agreeŌĆØ exceeded 2/3 of the responses.
Of the 10 final items, 9 items were passed with a passing vote of 2/3 or greater. However, key question 8 (Is continuous electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring necessary for high-risk patients undergoing endoscopic sedation? Statement: We suggest continuous ECG monitoring during endoscopic sedation to prevent fatal AEs in significantly high-risk patients (e.g., cardiovascular disease, arrhythmia, pulmonary disease, old age, requiring extended procedure [Evidence level C, Grade of recommendation III]) was removed as only 64.6% of experts agreed (Supplementary Table 2). The final statements are summarized in Table 3.
KEY QUESTIONS FOR THE EVALUATION OF PATIENTS BEFORE SEDATION AND PREPARATION OF SEDATIONQuestion 1. Is having at least one healthcare provider involved in sedation receiving basic life support (BLS) training effective in responding to the patientŌĆÖs adverse events?We recommend that physicians who administer endoscopic sedation and their assistant healthcare staff receive BLS training to prevent fatal progression of sedation AEs, such as death.
(Evidence level: D, Grade of recommendation: II, Expert consensus: 88.0%)
Background: Proper knowledge about sedation and fostering emergency response competencies through life support training are essential to ensure safe endoscopic sedation and timely response to sedation-related AEs. Life support training programs include BLS, advanced cardiac life support (ACLS), and Korean advanced life support (KALS). BLS comprises the initial steps in cardiopulmonary resuscitation, such as cardiac arrest confirmation, opening of the airway, artificial respiration, and chest compression. ACLS comprises basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation, electrical defibrillation, airway control, breathing support, and assessment. Diverse curricula are used by different countries and agencies to train physicians who administer endoscopic sedation. The need for education has been proposed by several clinical recommendations [1-3]. Furthermore, training healthcare providers involved in endoscopic sedation, including nurses, about emergency situations was effective in improving patient safety and the environment of the procedure [4]. Although prospective comparative studies on the effects of life support training have not been conducted, physicians and healthcare providers are recommended to undergo relevant training from a safety perspective, such as managing side effects and AEs.
Question 2. Can equipping the endoscopy unit with equipment and drugs for emergency resuscitation reduce fatal sedation-related adverse events in patients undergoing endoscopic sedation?We recommend equipping the endoscopy unit with equipment and drugs for emergency resuscitation, as fatal AEs, such as drug-related dyspnea, hypotension, and shock, may occur during endoscopic sedation.
(Evidence level: C, Grade of recommendation: II, Expert consensus: 94.4%)
Background: Most adverse drug reactions of sedatives used during endoscopic sedation are mild and temporary. However, life-threatening events, such as hypoxia, arrhythmia, and anaphylactic reactions, can occur in rare cases [5,6]. A prospective multicenter study involving 191,142 participants reported that sedation-related AEs occurred in 82 (0.00042%) patients, 6 (0.00003%) of whom died from respiratory failure, hypotension, or cardiac arrest [7]. A prospective study of 1,016 patients also observed cases of hypoxia (n=74, 7.3%), hypotension requiring pressor agents (n=8, 0.8%), and premature termination of the procedure (n=6, 0.6%) after sedative administration, with 141 (13.8%) patients requiring airway control [8]. In addition, one study reported that cardiovascular AEs that required atropine or antagonistic agents occurred during endoscopic sedation in approximately 2.7% of cases [9].
The ASGE, ESGE, and JGES CPGs recommend equipping the endoscopy unit with drugs and equipment needed for emergency resuscitation, along with periodic patient monitoring during endoscopic sedation. Korean Accredited Endoscopy Unit Certification Guidelines also recommend that endoscopy units should be equipped with emergency resuscitation devices (e.g., laryngeal masks or tracheal intubation equipment and defibrillators) and emergency medications (e.g., epinephrine, flumazenil, and naloxone) to be able to deal with emergency situations during endoscopic sedation. However, due to ethical and practical limitations in study design, currently there are no studies presenting data to conclude whether equipping the unit with drugs and equipment for emergency response can reduce the incidence of fatal sedation-related AEs. However, considering that most cases of sedative-associated deaths were induced by hypoxia and airway obstruction, as previously mentioned, it is necessary to equip the unit with appropriate emergency resuscitation equipment and drugs. Such readiness would allow healthcare providers to appropriately deal with abnormalities, such as abnormal vital signs, to reduce the incidence of fatal sedation-related AEs.
Question 3. Is assessing patientsŌĆÖ age, history, body mass index (BMI), Mallampati score, and American Society of Anesthesiologist (ASA) physical status class effective in preventing adverse events of endoscopic sedation?We recommend assessing the patientsŌĆÖ age, history, BMI, Mallampati score, and ASA physical status class to prevent AEs related to sedation.
(Evidence level: B, Grade of recommendation: II, Expert consensus: 79.2%)
Background: Sedation alleviates the patientŌĆÖs anxiety, discomfort, and pain during endoscopy and minimizes the unpleasant memory of discomfort or pain experienced during the procedure. Moreover, it ensures an environment where the endoscopist can concentrate on the procedure, thus facilitating a smooth procedure. However, as sedation can induce side effects, necessary measures should be taken to prevent them. Understanding the patient preprocedurally is part of such an effort.
PatientsŌĆÖ age, history, BMI, Mallampati classification, and ASA physical status class were associated with AEs of endoscopic sedation in multiple studies. Although the level of evidence is not high due to the lack of randomized controlled trials (RCTs), such pre-sedation assessment is beneficial in that it is easy for the patient. Thus, several CPGs consistently recommend such assessments [2,10,11].
Sedation-related AEs are more common in older patients. This was observed with various sedatives and endoscopic examinations [12-14]. Therefore, sedatives should be used with caution in older patients. However, there is no widely accepted standard for ŌĆ£old age,ŌĆØ and the ASGE CPGs did not present a clear-cut definition of the elderly either [11].
A history assessment involves checking various factors that may influence sedation, including sleep apnea, drug allergy, current medications used, history of sedation-related and anesthesia-related AEs, time of last oral feeding and type of food consumed, alcohol consumption, smoking, substance abuse, pregnancy, and breastfeeding status [2,15]. Cardiovascular diseases, kidney diseases, and liver diseases are also known risk factors for sedation-related AEs. Therefore, they must be checked [16]. BMI is an independent risk factor for sedation-related AEs. Many studies have confirmed that the incidence of AEs increases with increasing BMI [10]. No CPGs clearly define a high BMI. However, it is generally accepted that a BMI over 25 is considered a high-risk factor for hypoxia [14].
The Mallampati classification (Fig. 2) helps identify patients with potential sleep apnea and predicts challenging endotracheal intubation [17]. The ESGE CPGs recommend the primary involvement of an anesthesiologist for patients with a Mallampati class of 3 or higher [10]. Furthermore, the incidence of AEs increases with high ASA physical status classes (Table 4) [18,19]. Based on these, several CPGs recommend that endoscopists to consult an anesthesiologist [2,10,11]. However, the specific cut-off for anesthesiologist involvement varies across guidelines (class 3 or 4), making it practically difficult to adhere to such recommendations in the Korean clinical setting. Therefore, endoscopists should take more precautions when performing endoscopic sedation in these patients. The decision to consult an anesthesiologist should consider various factors, including the targeted depth of sedation, patientŌĆÖs state, and circumstances of the healthcare facility.
Question 4. Is reducing the dose of sedatives effective in lowering the incidence of severe adverse events associated with endoscopic sedation in older adults?We recommend reducing the initial and additional doses to reduce the incidence of severe AEs of endoscopic sedation in older adults.
(Evidence level: C, Grade of recommendation: II, Expert consensus: 93.2%)
Background: Although the definition of the elderly is not concrete, the United Nations (UN) uses the age of 65 years as the standard to determine an aged society and aging society. Korea became an aged society with a Ōēź65 years population exceeding 14% of the total population in 2017. In these CPGs, we define an older adult as a person aged Ōēź65 years. However, we do not strictly distinguish the recommended sedation strategies based on biological age in this guideline because biological age is a continuous variable that can differ between individuals.
Older adult shows an elevated susceptibility to sedatives due to various physiological changes [20]. As an individual ages, a ventilation-perfusion mismatch can result in reduced arterial oxygen saturation [21], and cardiopulmonary stimulation in response to hypoxia or hypercapnia is delayed or diminished. The incidence of respiratory depression and transient apnea caused by drugs that inhibit the central nervous system (CNS) also increases with age. The risk of aspiration increases with age due to the need for stronger stimuli to trigger the epiglottis reflex [22]. In addition, increasing fat fraction with aging can lead to an increased volume of distribution of lipid-soluble drugs such as benzodiazepines. Diminished hepatic and renal clearance rates result in a longer recovery time. Ultimately, the required dose of general sedatives is reduced due to increased CNS sensitivity, changes in drug receptors, changes in the volume of distribution, and inter-compartmental clearance.
However, age alone is not a key factor that increases the risk of sedation-related AEs. Other aging-related morbidities and rapid or excessive drug administration are known to have greater contributions to cardiopulmonary AEs associated with endoscopic sedation [20]. One prospective cohort study reported that the age group of Ōēź80 years had a significantly higher percentage of those with oxygen desaturation than the age group of <80 years after standard moderate sedation for colonoscopy (27% vs. 19%, p=0.007). Such oxygen desaturation was found to be associated with the dosage of meperidine (1.05 vs. 0.75 mg/kg) [23].
Thus, one of the first precautions to administer endoscopic sedation in older patients is to use a lower initial dose and administer it more slowly with a lower total dose [24-26]. ESGE and JGES CPGs for sedation and ASGE CPGs for endoscopy in older patients also mention the need to reduce the dose of sedatives [2,10,24]. Dosage calculated simply as mg per kg of body weight may induce serious respiratory depression and hypotension in older adults. Studies, particularly RCTs, on whether reducing the dose of sedatives can lead to a lower incidence of severe AEs are lacking. However, one prospective observational study reported that the same blood concentration and level of sedation were achieved with less than half of the dose (about 40%) in elderly patients aged Ōēź90 years compared to those aged <90 years [27]. Another prospective observational study also mentioned that the appropriate dose of sedatives for older adults was less than for younger individuals [28]. Furthermore, several prospective and retrospective studies - although the age of the study population and type of endoscopy varied - reported that the dose of sedatives needed to achieve a proper level of sedation was lower for older adults compared to that for younger ages and that the use of a higher dose of sedatives was associated with an increased incidence of AEs [26,27,29-32]. As for younger ages, midazolam or opioid analgesics are generally used for sedation in older patients. Fentanyl might be more beneficial for older patients because it can promote a rapid recovery due to quick onset of action and short half-life than meperidine [33]. While propofol has a narrower scope of safety in older patients, studies have documented that propofol can also be used relatively safely for older patients if it is used under continuous monitoring [27,28,33,34]. Evidence for reducing the dose of propofol according to age is lacking. However, one study investigated the propofol dose to maintain serum concentration in a 90-years-old person equivalent to a middle-aged person and found that approximately 40% dose of propofol in a 90-years-old person showed similar serum concentrations [27]. Therefore, endoscopic sedation can be performed safely for older adults aged 80 years by reducing the initial dose of a sedative to less than half of the standard dose, using a lower additional dose, administering drugs more slowly, and continuously monitoring the patient.
KEY QUESTIONS FOR INTRA-SEDATION AND OXYGEN SUPPLYQuestion 5. Is having exclusive sedation monitoring personnel effective in preventing fatal adverse events associated with endoscopic sedation?We suggest that properly trained personnel in addition to the endoscopist monitor sedation during endoscopic sedation to prevent fatal AEs during highly challenging endoscopic procedures or extended procedures.
(Evidence level: D, Recommendation grade: III, Expert consensus: 87.5%)
Background: Personnel who are involved only in sedation, not in endoscopy, during endoscopic sedation are referred to as sedation monitoring personnel. Physicians and nursing staff (registered nurses and nurse aids) can be designated as sedation monitoring personnel [35]. Physicians and nursing staff performing endoscopy and sedation monitoring personnel must complete a propofol-based sedation-related training certified by the Korea Medical Association to learn about sedation-related AEs. They must be well aware of appropriate patient monitoring methods, sedation dosing, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the drugs involved, drug interactions, potential AEs and management, and airway management methods [3,35].
Non-anesthesiologists (i.e., non-anesthesiologist physicians or nurses) administration of propofol (NAAP) is safe and effective in several types of endoscopic procedures that require moderate sedation [36-39]. Although high-quality data are lacking, one meta-analysis has shown that NAAP is as safe as the administration of propofol by an anesthesiologist in routine endoscopy for patients with ASA physical status classes IŌĆōII [40]. Routine endoscopy requiring moderate sedation can be performed adequately by one endoscopist, one nurse, and monitoring oxygen saturation [41]. As for sedated diagnostic upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in patients with ASA class I-III, sedation by anesthesiologists increases the incidence of sedation-related AEs. Sedation by anesthesiologists does not have safety benefits in colonoscopy [42]. It is not cost-effective for screening colonoscopy [43]. It can increase the risk of aspiration in colonoscopy [44] and elevate the overall risk of AEs [45]. Indications for consulting an anesthesiologist include ASA physical status class III or higher, challenging airway, severe obstructive pulmonary disease, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, and need for deep sedation [2,10,46].
Regarding sedation monitoring personnel, the 2010 ESGE CPGs recommended having sedation monitoring personnel during propofol-based sedation [47]. However, the revised 2015 ESGE CPGs did not strongly recommend it [10] because Swiss, German, and international surveys revealed that many countries performed endoscopic sedation without exclusive sedation monitoring staff, and the incidence of AEs did not increase markedly [7,38,48]. This does not mean that sedation monitoring staff is not needed. Instead, a neutral stance was taken, as there were mixed opinions among guideline authors regarding the need for sedation monitoring personnel in NAAP. The 2018 ASGE CPGs recommend that sedation monitoring personnel be provided during deep sedation using propofol [11]. The 2020 JGES CPGs recommend that sedation monitoring personnel be provided during challenging endoscopy, although the level of evidence was low [2]. In summary, although sedation monitoring personnel appear unnecessary for routine diagnostic esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), colonoscopy, and simple endoscopic procedures requiring moderate sedation, such as polypectomy, due to the low risk of AEs, sedation monitoring personnel would nevertheless help monitor the patientŌĆÖs state during sedation depending on various factors, such as deep sedation, patientŌĆÖs state, invasiveness of endoscopy, and proficiency of the endoscopist [35].
Consulting and receiving assistance from an anesthesiologist for challenging sedated endoscopic procedures is practically difficult in the Korean healthcare environment, except for a few tertiary healthcare facilities. However, a 2016 Korean survey on endoscopic sedation showed that at least two healthcare staffs in addition to the endoscopist were involved in endoscopic sedation in approximately 68.4% of cases [49], suggesting that it would be easier to implement sedation monitoring personnel in endoscopic sedation in Korea. Therefore, if endoscopic sedation is anticipated to be challenging, such as cases requiring deep sedation, challenging airways (obstructive sleep apnea, short neck, Mallampati grade III or higher, laryngopharyngeal tumor, BMI Ōēź30), ASA physical status class III or higher, extended duration of the procedure, highly invasive endoscopic procedure (endoscopic submucosal dissection, stent placement, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography [ERCP], endoscopic ultrasound and endoscopic ultrasound-guided procedure, small bowel enteroscopy), and history of sedation-related or anesthesia-related AEs, the implementation of sedation monitoring personnel, would be beneficial in clinical practice despite the lack of strong evidence.
Question 6. Is supplemental oxygen administration necessary for patients undergoing endoscopic sedation?We strongly recommend supplemental oxygen administration before and during endoscopic sedation to prevent severe hypoxia.
(Evidence level: A, Grade of recommendation: I, Expert consensus: 81.1%)
Background: Hypoxia is the most common and problematic AE associated with endoscopic sedation. All selected guidelines (ASGE, ESGE, and JGES CPGs) strongly recommend the administration of oxygen to prevent hypoxia during the procedure [2,10,11,35]. Several studies have shown that administration of oxygen can lower the incidence of hypoxia and increase oxygen saturation during the procedure in all age groups, including older adults, during EGD, colonoscopy, ERCP, and endoscopic ultrasound. Therefore, the administration of oxygen is essential to prevent hypoxia at all levels of sedation, including moderate and deep sedation [50-62].
Denitrogenation and preoxygenation are important for the prevention of hypoxia. The general method of oxygen administration during endoscopic sedation is to administer oxygen after administering sedatives. However, sedatives produce action within 30 seconds to 1 minute after administration. A delay in oxygen administration may lead to hypoxia. Thus, ŌĆ£preoxygenation,ŌĆØ where oxygen administration begins at 1ŌĆō2 minutes before the administration of sedatives, might be safer. A normal adult has a functional residual capacity (FRC) of approximately 2,500 mL, consuming approximately 250 mL of oxygen per minute. If the FRC includes approximately 500 mL of oxygen indoors, hypoxia will occur at approximately 2 minutes after inadequate ventilation with normal metabolic expenditure. If denitrogenation and preoxygenation are performed to reach 100% SpO2, an individual can theoretically survive for 10 minutes without respiration. Indeed, the calculation varies for obese patients or patients with pulmonary dysfunction. Although nasal administration of oxygen cannot lead to 100% denitrogenation even with preoxygenation, it can delay the onset of hypoxia. Based on some study findings that preoxygenation 1ŌĆō2 minutes before the procedure can prevent hypoxia in older adults at high risk for hypoxia, preoxygenation can be considered for at-risk group [60].
Question 7. Are assessments of the level of consciousness, pulse oximetry, and noninvasive blood pressure monitoring necessary during endoscopic sedation?We strongly recommend continuously assessing the level of consciousness, performing pulse oximetry, and performing noninvasive blood pressure monitoring during endoscopic sedation to enable early detection and treatment of sedation-related AEs.
(Evidence level: B, Grade of recommendation: I, Expert consensus: 94.0%)
Background: Endoscopic sedation may lead to AEs depending on the depth of sedation and sedatives used. AEs might be temporary. They may also progress to severe cardiopulmonary complications. Therefore, respiratory and circulatory monitoring are crucial to prevent them [63]. ASGE, ESGE, and JGES CPGs all recommend continuous monitoring of the level of consciousness, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure during endoscopic sedation to detect and treat sedation-related AEs early on [2,10,11].
The depth of sedation differs according to the type of sedative, type of endoscopic procedure, difficulty of the procedure, and patientŌĆÖs status. Sedation dosing should be adjusted by repeatedly assessing the patientŌĆÖs level of consciousness to determine whether the targeted sedation depth has been achieved (four levels of sedation by ASA, Table 5) [64].
There are a few methods to assess the level of consciousness of patients, including the four levels of sedation proposed by the ASA, modified observerŌĆÖs assessment of alertness and sedation (MOAA/S) scale (Table 6), and Ramsay Sedation Scale. The four levels of sedation proposed by the ASA are difficult to utilize during the procedure. Therefore, the MOAA/S scale or the Ramsay Sedation Scale can be used for intraprocedural sedation assessment. The accredited endoscopy unit certification system by KSGE uses the MOAA/S scale. The patientŌĆÖs level of consciousness must be continuously assessed using sedation scales.
Moderate and deep sedation require periodic assessments of the patientŌĆÖs level of consciousness and vital signs. It is recommended to monitor them at a minimum of 5-minute intervals before sedation, immediately after administering sedatives, during sedation, during recovery, and before discharge [11,65]. For respiratory monitoring, it is important to check breathing status and respiratory rate. Monitoring oxygen saturation through pulse oximetry is recommended for all patients, as it helps prevent AEs by early detection of hypoxia [64,66,67]. Circulatory monitoring involves periodically measuring blood pressure using a noninvasive blood pressure monitor. It enables early detection of hypotension [64,68]. Pulse oximetry and noninvasive blood pressure monitoring are inexpensive and easy to use. Therefore, they are recommended for use in all patients undergoing endoscopic sedation [2,10,11].
Although there are no RCTs assessing the level of consciousness or monitoring oxygen saturation and blood pressure in patients undergoing endoscopic sedation, an European survey has reported that the use of blood pressure and oxygen saturation monitoring has consistently increased over the past decades. Currently, measuring blood pressure and oxygen saturation during sedation is standard practice [38]. A Spanish study in 2014 reported that 99.6% and 86.7% of endoscopy units were equipped with a pulse oximeter and blood pressure cuff, respectively [69]. A German survey performed in 2010 reported that oxygen saturation was measured using a pulse oximeter in 97% of patients who underwent endoscopic sedation [70]. A Korean study in 2016 showed that 94.1% of healthcare facilities measured oxygen saturation using a pulse oximeter (100% in university hospitals and 91.8% in non-university hospitals) [49]. The safety of endoscopic sedation can be ensured through continuous assessment of the level of consciousness and measurement of oxygen saturation using a pulse oximeter and noninvasive blood pressure monitoring.
KEY QUESTIONS FOR AFTER SEDATION AND PREPARATION FOR DISCHARGEQuestion 8. Is the application of appropriate criteria for discharge from the post-endoscopy recovery room effective in preventing adverse events after sedation?We suggest that appropriate criteria should be established to determine a patientŌĆÖs readiness for discharge to ensure safe recovery and that the level of consciousness, appendicular skeletal muscle activity, respiration, circulation, and oxygen saturation should be considered as criteria for discharge.
(Evidence level: D, Grade of recommendation: III, Expert consensus: 91.5%)
Background: After endoscopic sedation, patients should be monitored for abnormal signs [71]. After the procedure, it is imperative that properly trained personnel monitor a patientŌĆÖs cardiopulmonary function in an independent recovery room equipped with appropriate monitoring and resuscitation equipment [15,65]. It would be desirable to establish standardized discharge criteria to determine post-sedation recovery. The most common systems used to assess post-endoscopic recovery are the Aldrete scoring system and the modified post-anesthesia discharge scoring system (mPADSS) (Table 7). The Aldrete scoring system assesses a patient based on respiration, oxygen saturation, blood pressure, level of consciousness, and appendicular skeletal muscle activity [72,73]. mPADSS uses circulation (blood pressure and pulse), mobility, nausea and vomiting, pain, and bleeding at the procedure site as criteria [74,75]. These two systems were developed as indicators for post-anesthesia recovery after outpatient surgeries. However, they are currently the most widely used methods to assess recovery after endoscopic sedation. The discharge criteria should be appropriate to the context of each endoscopy recovery room, focusing on ensuring post-sedation recovery and safe discharge [76,77].
Data supporting recovery time by the type of drug used are lacking. There was no significant difference in the degree of consciousness recovery, quality of consciousness recovery, or time of discharge between the use of propofol and the use of opioid analgesics with midazolam [78,79]. The combined use of traditional sedatives and propofol tends to shorten recovery and promote early discharge [80].
Question 9. Should patients be accompanied by a caregiver when presenting with endoscopic sedation?We recommend that patients who undergo endoscopic sedation be accompanied by a caregiver to assist with safe discharge, as psychomotor and cognitive impairments can occur after sedation.
(Evidence level: C, Grade of recommendation: II, Expert consensus: 81.4%)
Background: Patients who undergo endoscopic sedation may experience psychomotor and cognitive impairments after the procedure. A prospective study of 31 patients who underwent sedated EGD using midazolam and meperidine reported that the psychomotor functions of the patients were impaired by an average of 30ŌĆō40% compared to their pre-sedation state, even though they met the discharge criteria [71]. They should be accompanied by a caregiver at discharge, as patients are at risk of experiencing sedation-related AEs after discharge due to impaired psychomotor and cognitive functions. The ESGE guidelines also strongly recommend that patients be accompanied by a caregiver upon discharge after endoscopic sedation. Furthermore, the 2016 clinical recommendations for propofol-based sedation for physicians in Korean healthcare clinics and hospitals recommend that patients who undergo propofol-based sedation should be accompanied by a caregiver to ensure safe discharge and availability of a person who can contact the clinic or hospital upon onset of sedation-related AEs after discharge [35]. Caregivers include family members, relatives, and friends who can help with safe discharge of the patient after endoscopic sedation. However, there are no established guidelines on whether only family members and relatives who can take responsibility in case of an accident should be eligible caregivers. Therefore, the eligibility of a caregiver should be determined based on the internal policies of each facility.
The degree of psychomotor and cognitive impairment after discharge varies according to the sedatives and combinations of drugs used for endoscopic sedation. In particular, using a drug with a relatively longer duration of action and half-life, such as midazolam and opioid analgesics, can lead to more severe impairment of psychomotor and cognitive functions than propofol alone. A prospective study that performed minimal sedation with midazolam alone in 30 patients undergoing colonoscopy reported that 25 patients showed clear cognitive impairment even 2 hours after the procedure [81]. Furthermore, in a prospective study of three combined regimens (midazolam/fentanyl, midazolam/fentanyl/propofol, and midazolam/propofol) in patients undergoing EGD and colonoscopy consecutively, all three groups showed cognitive impairment at discharge, with the dosage of midazolam and fentanyl having a marked effect on cognitive impairment [79]. Meanwhile, sedation with propofol alone led to relatively fewer cases of cognitive impairment compared to midazolam alone or a combination of midazolam with another drug. According to one Japanese study, approximately 92% of 400 patients who received low-dose propofol-based sedation for EGD safely drove home after discharge [82]. A prospective study conducted on patients who underwent colonoscopy with propofol alone sedation also observed that patientsŌĆÖ psychomotor function, driving ability, and blood propofol concentration returned to normal levels within 1 hour after the procedure [83]. Similarly, 65% of 2,101 patients who underwent propofol alone sedation for colonoscopy safely drove home themselves [84]. An RCT that compared propofol alone, propofol/fentanyl, and midazolam/fentanyl regimens reported that the propofol alone group had minimal cognitive impairments [85]. According to a recent RCT on 415 patients who underwent sedated colonoscopy, the propofol alone group (n=205) showed relatively less cognitive impairment at 1 hour after the procedure than the combined midazolam/propofol group (n=210) [78]. There are details on sedatives for endoscopic sedation in A Guidebook on Endoscopic Sedation 2021 Revised Edition published by KSGE. For more information on sedatives, please refer to this guidebook.
Designing RCTs to prove that having patients be accompanied by a caregiver upon discharge after endoscopic sedation can lower the incidence of sedation-related AEs is practically and ethically impossible. However, several studies have reported that patients show psychomotor and cognitive impairments compared to pre-sedation levels, even though the discharge criteria are met. Because this may hinder safe discharge, we recommend that patients should be accompanied by a caregiver at discharge. Midazolam and opioid analgesics with relatively longer durations of action and half-life tend to cause more severe psychomotor and cognitive impairment after sedation. However, sedation with propofol alone may also cause such impairments. Therefore, having a caregiver is essential. In general, family members can serve as caregivers. The specific definition of a caregiver will be addressed in the subsequent update considering the reality in Korea.
CONCLUSIONThe use of endoscopic sedation is expected to increase in the coming years due to its benefits, such as alleviating the anxiety of patients, thus boosting their willingness to undergo testing in the future and ensuring a relaxed and comfortable environment for the endoscopist to perform the procedure. International CPGs for endoscopic sedation mostly deal with two aspects of endoscopic sedation: efficiency and safety. However, the details of efficient endoscopic sedation that involve the choice of sedative, dosage, administration, and use of music during sedation can differ across countries. However, this remains controversial. Therefore, we focused on the safety aspect of endoscopic sedation in these CPGs and present the minimal criteria to ensure safe sedation procedures. Further accumulation of clinical evidence in Korea would enable the inclusion of content for efficient endoscopic sedation. Although it was not easy to present consistent criteria due to differences in the type of healthcare facility, region, physician-nurse, and individual experiences, adhering to the safety criteria delineated in these CPGs to prevent severe AEs would allow endoscopists to provide safer sedated endoscopic procedures.
NOTES
Conflicts of Interest: Jae Min Lee and Hyung Ku Chon are currently serving in KSGE Publication Committee; however, they were not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. Other authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding
Any costs for literature searching, conferences, and other statistical activities were covered by a research fund provided by the KSGE. The KSGE supported the development of these guidelines. However, this organization did not influence the content of the guidelines.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Byung-Wook Kim
Data curation: B-WK
Formal analysis: Hong Jun Park, Jun Kyu Lee, Yehyun Park, Jin Myung Park, Jun Yong Bae, Seung Young Seo, Jae Min Lee, Jee Hyun Lee, Hyung Ku Chon, Jun-Won Chung, Hyun Ho Choi
Investigation: HJP, JKL, YP, JMP, JYB, SYS, JML, JHL, HKC, J-WC, HHC, Myung Ha Kim
Methodology: Dong Ah Park, Jae Hung Jung
Project administration: B-WK, Joo Young Cho
Resources: HJP, JKL, YP, JMP, JYB, SYS, JML, JHL, HKC, J-WC, HHC, MHK
Supervision: B-WK, JYC
Validation: B-WK, JYC
Visualization: HJP, JKL, YP, JMP, JYB, SYS, JML, JHL, HKC, J-WC, HHC
Writing the original draft: HJP, JKL, YP, JMP, JYB, SYS, JML, JHL, HKC, J-WC, HHC
Writing-review & editing: B-WK, JYC
Fig.┬Ā1.PRISMA flow chart for selecting reference clinical practice guidelines. KoMCI, Korea Medical Citation Index; NICE, National Institute of Health and Care Excellence; WHO, World Health Organization. 
Fig.┬Ā2.Mallampati classification of airways. The patient is assessed while sitting up with the mouth opened wide and tongue protruded as much as possible. 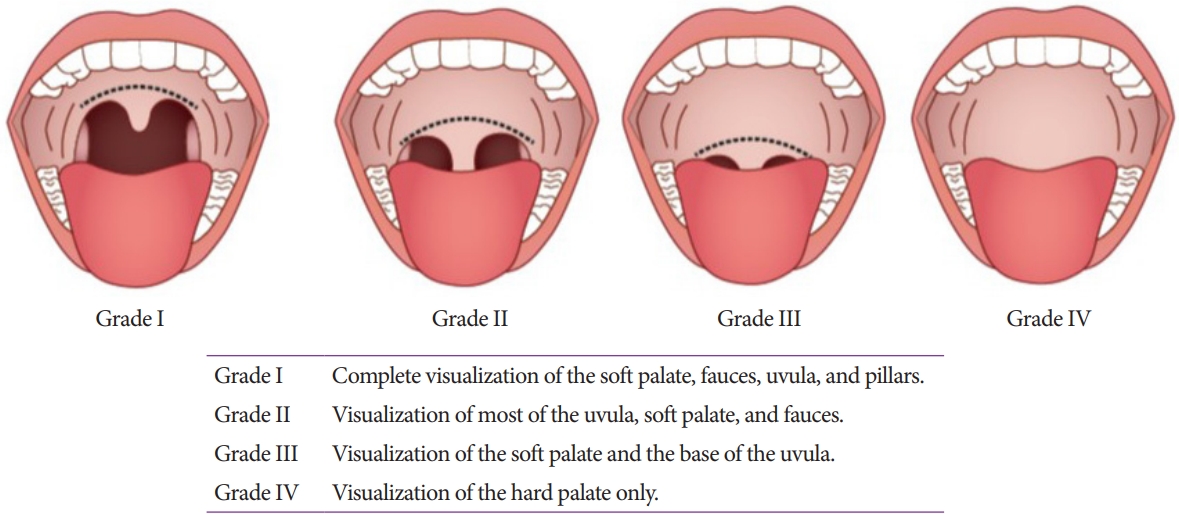
Table┬Ā1.Level of Evidence Table┬Ā2.Grade of Recommendation Table┬Ā3.Summary of Statements, Grade of Recommendation, and Level of Evidence Table┬Ā4.American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status Classification (https://www.asahq.org/standards-and-guidelines/asa-physical-status-classification-system) Table┬Ā5.Level of Sedation by American Society of Anesthesiologists Table┬Ā6.Modified ObserverŌĆÖs Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale Table┬Ā7.Criteria for Discharge from the Post-Endoscopy Recovery Room REFERENCES1. Dumonceau JM, Riphaus A, Beilenhoff U, et al. European curriculum for sedation training in gastrointestinal endoscopy: position statement of the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) and European Society of Gastroenterology and Endoscopy Nurses and Associates (ESGENA). Endoscopy 2013;45:496ŌĆō504.
2. Gotoda T, Akamatsu T, Abe S, et al. Guidelines for sedation in gastroenterological endoscopy (second edition). Dig Endosc 2021;33:21ŌĆō53.
3. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; American College of Gastroenterology; American Gastroenterological Association Institute, et al. Multisociety sedation curriculum for gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2012;76:e1ŌĆōe25.
4. Schilling D, Leicht K, Beilenhoff U, et al. Impact of S3 training courses ŌĆ£Sedation and emergency management in endoscopy for endoscopy nurses and assisting personnelŌĆØ on the process and structure quality in gastroenterological endoscopy in practices and clinics - results of a nationwide survey. Z Gastroenterol 2013;51:619ŌĆō627.
5. Berzin TM, Sanaka S, Barnett SR, et al. A prospective assessment of sedation-related adverse events and patient and endoscopist satisfaction in ERCP with anesthesiologist-administered sedation. Gastrointest Endosc 2011;73:710ŌĆō717.
6. Qadeer MA, Lopez AR, Dumot JA, Vargo JJ. Hypoxemia during moderate sedation for gastrointestinal endoscopy: causes and associations. Digestion 2011;84:37ŌĆō45.
7. Frieling T, Heise J, Kreysel C, Kuhlen R, Schepke M. Sedation-associated complications in endoscopy--prospective multicentre survey of 191142 patients. Z Gastroenterol 2013;51:568ŌĆō572.
8. Wani S, Azar R, Hovis CE, et al. Obesity as a risk factor for sedation-related complications during propofol-mediated sedation for advanced endoscopic procedures. Gastrointest Endosc 2011;74:1238ŌĆō1247.
9. Mador MJ, Nadler J, Mreyoud A, et al. Do patients at risk of sleep apnea have an increased risk of cardio-respiratory complications during endoscopy procedures? Sleep Breath 2012;16:609ŌĆō615.
10. Dumonceau JM, Riphaus A, Schreiber F, et al. Non-anesthesiologist administration of propofol for gastrointestinal endoscopy: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, European Society of Gastroenterology and Endoscopy Nurses and Associates guideline--updated June 2015. Endoscopy 2015;47:1175ŌĆō1189.
11. ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Early DS, Lightdale JR, et al. Guidelines for sedation and anesthesia in GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2018;87:327ŌĆō337.
12. Friedrich K, Stremmel W, Sieg A. Endoscopist-administered propofol sedation is safe - a prospective evaluation of 10,000 patients in an outpatient practice. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 2012;21:259ŌĆō263.
13. Kim SY, Moon CM, Kim MH, et al. Impacts of age and sedation on cardiocerebrovascular adverse events after diagnostic GI endoscopy: a nationwide population-based study. Gastrointest Endosc 2020;92:591ŌĆō602.e16.
14. Mehta PP, Kochhar G, Kalra S, et al. Can a validated sleep apnea scoring system predict cardiopulmonary events using propofol sedation for routine EGD or colonoscopy? A prospective cohort study. Gastrointest Endosc 2014;79:436ŌĆō444.
15. Cha JM, Jeun JW, Pack KM, et al. Risk of sedation for diagnostic esophagogastroduodenoscopy in obstructive sleep apnea patients. World J Gastroenterol 2013;19:4745ŌĆō4751.
16. Hinkelbein J, Lamperti M, Akeson J, et al. European Society of Anaesthesiology and European Board of Anaesthesiology guidelines for procedural sedation and analgesia in adults. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2018;35:6ŌĆō24.
17. Mallampati SR, Gatt SP, Gugino LD, et al. A clinical sign to predict difficult tracheal intubation: a prospective study. Can Anaesth Soc J 1985;32:429ŌĆō434.
18. Dietrich CG, Kottmann T, Diedrich A, Drouven FM. Sedation-associated complications in endoscopy are not reduced significantly by implementation of the German S-3-guideline and occur in a severe manner only in patients with ASA class III and higher. Scand J Gastroenterol 2013;48:1082ŌĆō1087.
19. Enestvedt BK, Eisen GM, Holub J, Lieberman DA. Is the American Society of Anesthesiologists classification useful in risk stratification for endoscopic procedures? Gastrointest Endosc 2013;77:464ŌĆō471.
20. Muravchick S. The elderly outpatient: current anesthetic implications. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2002;15:621ŌĆō625.
21. Boss GR, Seegmiller JE. Age-related physiological changes and their clinical significance. West J Med 1981;135:434ŌĆō440.
22. Shaker R, Ren J, Bardan E, et al. Pharyngoglottal closure reflex: characterization in healthy young, elderly and dysphagic patients with predeglutitive aspiration. Gerontology 2003;49:12ŌĆō20.
23. Lukens FJ, Loeb DS, Machicao VI, Achem SR, Picco MF. Colonoscopy in octogenarians: a prospective outpatient study. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97:1722ŌĆō1725.
24. ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Chandrasekhara V, Early DS, et al. Modifications in endoscopic practice for the elderly. Gastrointest Endosc 2013;78:1ŌĆō7.
25. Darling E. Practical considerations in sedating the elderly. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am 1997;9:371ŌĆō380.
26. Peacock JE, Lewis RP, Reilly CS, Nimmo WS. Effect of different rates of infusion of propofol for induction of anaesthesia in elderly patients. Br J Anaesth 1990;65:346ŌĆō352.
27. Horiuchi A, Nakayama Y, Tanaka N, Ichise Y, Katsuyama Y, Ohmori S. Propofol sedation for endoscopic procedures in patients 90 years of age and older. Digestion 2008;78:20ŌĆō23.
28. Heuss LT, Schnieper P, Drewe J, Pflimlin E, Beglinger C. Conscious sedation with propofol in elderly patients: a prospective evaluation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003;17:1493ŌĆō1501.
29. Bell GD, Spickett GP, Reeve PA, Morden A, Logan RF. Intravenous midazolam for upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a study of 800 consecutive cases relating dose to age and sex of patient. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1987;23:241ŌĆō243.
30. Cha JM, Kozarek RA, La Selva D, et al. Risks and benefits of colonoscopy in patients 90 years or older, compared with younger patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;14:80ŌĆō86.e1.
31. Kazama T, Takeuchi K, Ikeda K, et al. Optimal propofol plasma concentration during upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in young, middle-aged, and elderly patients. Anesthesiology 2000;93:662ŌĆō669.
32. Mart├Łnez JF, Aparicio JR, Compa├▒y L, et al. Safety of continuous propofol sedation for endoscopic procedures in elderly patients. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2011;103:76ŌĆō82.
33. Hayee B, Dunn J, Loganayagam A, et al. Midazolam with meperidine or fentanyl for colonoscopy: results of a randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;69:681ŌĆō687.
34. Cohen LB, Hightower CD, Wood DA, Miller KM, Aisenberg J. Moderate level sedation during endoscopy: a prospective study using low-dose propofol, meperidine/fentanyl, and midazolam. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;59:795ŌĆō803.
35. Korean Medical Association. 2016 clinical recommendations for propofol-based sedation for physicians in Korean healthcare clinics and hospitals (in Korean). 2016 [Internet]. Seoul: KMA; c2016 [cited 2022 Jan 24]. Available from: https://www.nsdoctor.co.kr/file_download.php?idx=2384.
36. Cohen LB, Dubovsky AN, Aisenberg J, Miller KM. Propofol for endoscopic sedation: a protocol for safe and effective administration by the gastroenterologist. Gastrointest Endosc 2003;58:725ŌĆō732.
37. Fatima H, DeWitt J, LeBlanc J, Sherman S, McGreevy K, Imperiale TF. Nurse-administered propofol sedation for upper endoscopic ultrasonography. Am J Gastroenterol 2008;103:1649ŌĆō1656.
38. Heuss LT, Froehlich F, Beglinger C. Nonanesthesiologist-administered propofol sedation: from the exception to standard practice. Sedation and monitoring trends over 20 years. Endoscopy 2012;44:504ŌĆō511.
39. Jensen JT, Vilmann P, Horsted T, et al. Nurse-administered propofol sedation for endoscopy: a risk analysis during an implementation phase. Endoscopy 2011;43:716ŌĆō722.
40. Daza JF, Tan CM, Fielding RJ, Brown A, Farrokhyar F, Yang I. Propofol administration by endoscopists versus anesthesiologists in gastrointestinal endoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of patient safety outcomes. Can J Surg 2018;61:226ŌĆō236.
41. K├╝lling D, Orlandi M, Inauen W. Propofol sedation during endoscopic procedures: how much staff and monitoring are necessary? Gastrointest Endosc 2007;66:443ŌĆō449.
42. Vargo JJ, Niklewski PJ, Williams JL, Martin JF, Faigel DO. Patient safety during sedation by anesthesia professionals during routine upper endoscopy and colonoscopy: an analysis of 1.38 million procedures. Gastrointest Endosc 2017;85:101ŌĆō108.
43. Khiani VS, Soulos P, Gancayco J, Gross CP. Anesthesiologist involvement in screening colonoscopy: temporal trends and cost implications in the medicare population. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;10:58ŌĆō64.e1.
44. Cooper GS, Kou TD, Rex DK. Complications following colonoscopy with anesthesia assistance: a population-based analysis. JAMA Intern Med 2013;173:551ŌĆō556.
45. Wernli KJ, Brenner AT, Rutter CM, Inadomi JM. Risks associated with anesthesia services during colonoscopy. Gastroenterology 2016;150:888ŌĆō894; quiz e18.
46. Practice guidelines for moderate procedural sedation and analgesia 2018: a report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on moderate procedural sedation and analgesia, the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial surgeons, American College of Radiology, American Dental Association, American Society of Dentist Anesthesiologists, and Society of Interventional Radiology. Anesthesiology 2018;128:437ŌĆō479.
47. Dumonceau JM, Riphaus A, Aparicio JR, et al. European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, European Society of Gastroenterology and Endoscopy Nurses and Associates, and the European Society of Anaesthesiology guideline: non-anesthesiologist administration of propofol for gi endoscopy. Endoscopy 2010;42:960ŌĆō974.
48. Riphaus A, Macias-Gomez C, Devi├©re J, Dumonceau JM. Propofol, the preferred sedation for screening colonoscopy, is underused. Results of an international survey. Dig Liver Dis 2012;44:389ŌĆō392.
49. Lee CK, Dong SH, Kim ES, et al. Room for quality improvement in endoscopist-directed sedation: results from the first nationwide survey in Korea. Gut Liver 2016;10:83ŌĆō94.
50. Bell GD, Bown S, Morden A, Coady T, Logan RF. Prevention of hypoxaemia during upper-gastrointestinal endoscopy by means of oxygen via nasal cannulae. Lancet 1987;1:1022ŌĆō1024.
51. Bell GD, Quine A, Antrobus JH, et al. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a prospective randomized study comparing continuous supplemental oxygen via the nasal or oral route. Gastrointest Endosc 1992;38:319ŌĆō325.
52. Bowling TE, Hadjiminas CL, Polson RJ, Baron JH, Foale RA. Effects of supplemental oxygen on cardiac rhythm during upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a randomised controlled double blind trial. Gut 1993;34:1492ŌĆō1497.
53. Crantock L, Cowen AE, Ward M, Roberts RK. Supplemental low flow oxygen prevents hypoxia during endoscopic cholangiopancreatography. Gastrointest Endosc 1992;38:418ŌĆō420.
54. Zuccaro G, Radaelli F, Vargo J, et al. Routine use of supplemental oxygen prevents recognition of prolonged apnea during endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2000;51:AB141.
55. Griffin SM, Chung SC, Leung JW, Li AK. Effect of intranasal oxygen on hypoxia and tachycardia during endoscopic cholangiopancreatography. BMJ 1990;300:83ŌĆō84.
56. Gross JB, Long WB. Nasal oxygen alleviates hypoxemia in colonoscopy patients sedated with midazolam and meperidine. Gastrointest Endosc 1990;36:26ŌĆō29.
57. Haines DJ, Bibbey D, Green JR. Does nasal oxygen reduce the cardiorespiratory problems experienced by elderly patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography? Gut 1992;33:973ŌĆō975.
58. Iwao T, Toyonaga A, Shigemori H, Sumino M, Oho K, Tanikawa K. Supplemental oxygen during endoscopic variceal ligation: effects on arterial oxygenation and cardiac arrhythmia. Am J Gastroenterol 1995;90:2186ŌĆō2190.
59. Jurell KR, OŌĆÖConnor KW, Slack J, et al. Effect of supplemental oxygen on cardiopulmonary changes during gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 1994;40:665ŌĆō670.
60. Kim H, Hyun JN, Lee KJ, Kim HS, Park HJ. Oxygenation before endoscopic sedation reduces the hypoxic event during endoscopy in elderly patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Med 2020;9:3282.
61. Patterson KW, Noonan N, Keeling NW, Kirkham R, Hogan DF. Hypoxemia during outpatient gastrointestinal endoscopy: the effects of sedation and supplemental oxygen. J Clin Anesth 1995;7:136ŌĆō140.
62. Rozario L, Sloper D, Sheridan MJ. Supplemental oxygen during moderate sedation and the occurrence of clinically significant desaturation during endoscopic procedures. Gastroenterol Nurs 2008;31:281ŌĆō285.
63. Standards of Practice Committee of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, Lichtenstein DR, Jagannath S, et al. Sedation and anesthesia in GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2008;68:815ŌĆō826.
64. American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on sedation and analgesia by non-anesthesiologists. Practice guidelines for sedation and analgesia by non-anesthesiologists. Anesthesiology 2002;96:1004ŌĆō1017.
65. ASGE Ensuring Safety in the Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Unit Task Force, Calderwood AH, Chapman FJ, et al. Guidelines for safety in the gastrointestinal endoscopy unit. Gastrointest Endosc 2014;79:363ŌĆō372.
66. Cohen LB, Delegge MH, Aisenberg J, et al. AGA Institute review of endoscopic sedation. Gastroenterology 2007;133:675ŌĆō701.
67. Waring JP, Baron TH, Hirota WK, et al. Guidelines for conscious sedation and monitoring during gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2003;58:317ŌĆō322.
68. Maurer WG, Walsh M, Viazis N. Basic requirements for monitoring sedated patients: blood pressure, pulse oximetry, and EKG. Digestion 2010;82:87ŌĆō89.
69. Lucendo AJ, Gonz├Īlez-Huix F, Tenias JM, et al. Gastrointestinal endoscopy sedation and monitoring practices in Spain: a nationwide survey in the year 2014. Endoscopy 2015;47:383ŌĆō390.
70. Riphaus A, Rabofski M, Wehrmann T. Endoscopic sedation and monitoring practice in Germany: results from the first nationwide survey. Z Gastroenterol 2010;48:392ŌĆō397.
71. Willey J, Vargo JJ, Connor JT, Dumot JA, Conwell DL, Zuccaro G. Quantitative assessment of psychomotor recovery after sedation and analgesia for outpatient EGD. Gastrointest Endosc 2002;56:810ŌĆō816.
72. Aldrete JA. Modifications to the postanesthesia score for use in ambulatory surgery. J Perianesth Nurs 1998;13:148ŌĆō155.
75. Chung F, Chan VW, Ong D. A post-anesthetic discharge scoring system for home readiness after ambulatory surgery. J Clin Anesth 1995;7:500ŌĆō506.
76. Amornyotin S, Chalayonnavin W, Kongphlay S. Recovery pattern and home-readiness after ambulatory gastrointestinal endoscopy. J Med Assoc Thai 2007;90:2352ŌĆō2358.
77. Trevisani L, Cifal├Ā V, Gilli G, Matarese V, Zelante A, Sartori S. Post-anaesthetic discharge scoring system to assess patient recovery and discharge after colonoscopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2013;5:502ŌĆō507.
78. Gurunathan U, Rahman T, Williams Z, et al. Effect of midazolam in addition to propofol and opiate sedation on the quality of recovery after colonoscopy: a randomized clinical trial. Anesth Analg 2020;131:741ŌĆō750.
79. Thompson R, Seck V, Riordan S, Wong S. Comparison of the effects of midazolam/fentanyl, midazolam/propofol, and midazolam/fentanyl/ propofol on cognitive function after gastrointestinal endoscopy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 2019;29:441ŌĆō446.
80. Zhang K, Xu H, Li HT. Safety and efficacy of propofol alone or in combination with other agents for sedation of patients undergoing colonoscopy: an updated meta-analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2020;24:4506ŌĆō4518.
81. Hsu YH, Lin FS, Yang CC, Lin CP, Hua MS, Sun WZ. Evident cognitive impairments in seemingly recovered patients after midazolam-based light sedation during diagnostic endoscopy. J Formos Med Assoc 2015;114:489ŌĆō497.
82. Horiuchi A, Nakayama Y, Hidaka N, Ichise Y, Kajiyama M, Tanaka N. Low-dose propofol sedation for diagnostic esophagogastroduodenoscopy: results in 10,662 adults. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:1650ŌĆō1655.
83. Horiuchi A, Nakayama Y, Fujii H, Katsuyama Y, Ohmori S, Tanaka N. Psychomotor recovery and blood propofol level in colonoscopy when using propofol sedation. Gastrointest Endosc 2012;75:506ŌĆō512.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
