An unwonted complication of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Article information
Quiz
A 45-year-old man was admitted for the follow-up of benign biliary stricture after an episode of severe acute pancreatitis. He underwent endoscopic retrograde cholangiography (ERCP) three months prior. At that time, biliary sphincterotomy and stenting with a 10-Fr 7-cm stent (Cotton-Leung Biliary Stent; Cook Medical LLC, Bloomington, IN, USA) were performed, without complications. He had been abstinent from alcohol for the past eight months. He had no fever or abdominal pain. Abdominal examination showed a non-tender, flat abdomen. Complete blood count and liver function test results were all within normal ranges. Abdominal radiography revealed a biliary stent in the right upper quadrant (Fig. 1A). From abdominal computed tomography, the distal end of the biliary stent seemed to be slightly above the ampulla (Fig. 1B). ERCP was performed (Fig. 1C, D).
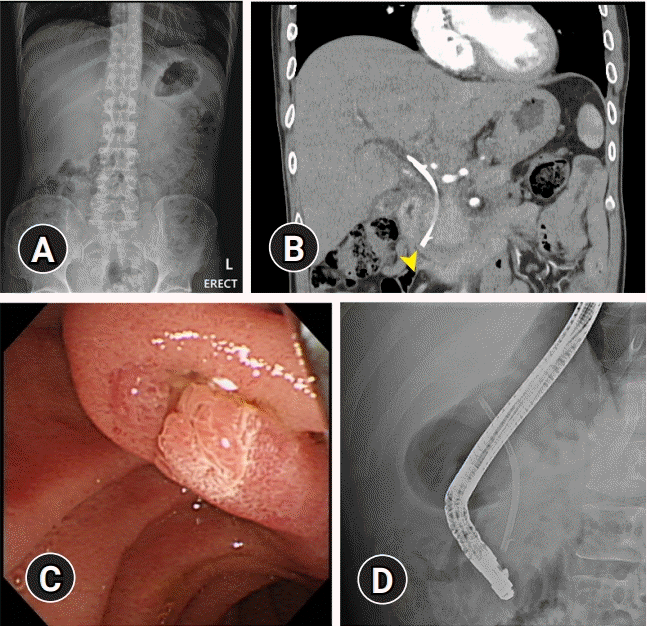
(A) Abdominal X-ray showed a biliary stent in the right upper quadrant. (B) Abdominal computed tomography revealed the biliary stent to be slightly above the ampulla (arrowhead). (C) Examination with the side-viewing duodenoscope showed evidence of prior sphincterotomy but no biliary stent at the bile duct orifice. (D) On fluoroscopy, the distal end of the biliary stent was located above the ampulla.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer
The patient was diagnosed with biliary stent migration. Initial attempts at stent removal were unsuccessful, despite endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation and the use of a stone retrieval basket, stone extraction balloon, and biopsy forceps. Therefore, a 5-Fr nasobiliary drainage catheter was inserted. After two days, ERCP was repeated. This time, a 0.035-inch guidewire was inserted into the stent lumen (Fig. 2A), and a 7-Fr Soehendra stent retriever was placed over the guidewire (Fig. 2B). The proximal end of the stent retriever was screwed to the distal end of the migrated stent (Fig. 2C). Under endoscopic and fluoroscopic guidance, both the stent and the stent retriever were pulled back slowly (Fig. 2D). When the distal flap of the stent was outside the major duodenal papilla, the stent retriever was dislodged and the stent was successfully removed using a snare. Cholangiogram showed a persistent biliary stricture. Therefore, a 10-Fr 7-cm biliary stent with multiple radial flaps (ST-2 Soehendra Tannenbaum Biliary Stent; Cook Medical LLC, Bloomington, IN, USA) was placed. The patient was discharged, without complications. A follow-up ERCP was performed three months later showing improvement of the biliary stricture.
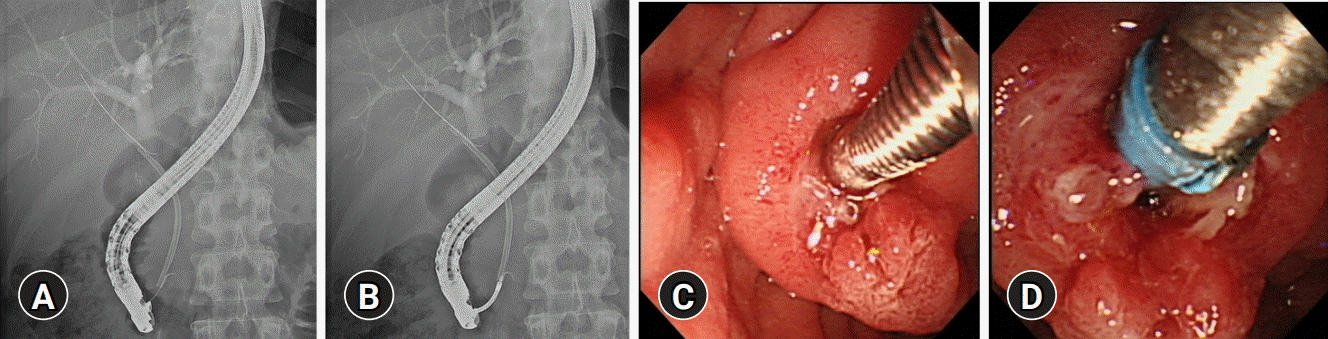
(A) A 0.035-inch guidewire was cannulated into the stent lumen. (B) A 7-Fr Soehendra stent retriever, which was placed over the guidewire, was screwed into the distal end of the stent. (C, D) Under endoscopic and fluoroscopic guidance, both the stent and the stent retriever were slowly pulled back into the duodenal lumen.
Biliary stent migration is one of the late complications of stent insertion. This occurs in approximately 5% of biliary stentings.1 Stent migration is more frequent in benign biliary strictures and with single-stent placements.1,2 Proximal biliary stent migration is associated with short stent length and distal biliary stricture.2 It is mostly asymptomatic and often detected during ERCP.2,3 However, adverse events can occur, including acute cholangitis, jaundice, intestinal obstruction and perforation, acute appendicitis, fistula formation, pneumonitis, and hepatic perforation.2 Therefore, when detected, a migrated stent should be removed. Various accessories can be utilized for the removal of a proximally migrated stent: stone extraction balloon catheter, stone retrieval basket, dilatation balloon, forceps, snare with a guidewire, and Soehendra stent retriever with a guidewire.2-5 In a retrospective multicenter study, the reported success rate of proximally migrated biliary stent removal was 71.4%.5 However, the reported success rate of distally migrated biliary stent removal was 100%.5 When a proximally migrated biliary stent removal is unsuccessful with the use of the above-mentioned accessories, digital single-operator cholangioscopy can be used to remove the migrated plastic and metallic biliary stents under direct visualization.3
Notes
Conflicts of Interest
Jimin Han is currently serving as a CE Quiz Editor; however, Jimin Han was not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this manuscript. Han Taek Jeong and Ho Gak Kim have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding
None.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: HTJ, HGK, JH; Data curation: HTJ, HGK, JH; Investigation: HTJ, HGK, JH; Writing-original draft: JH; Writing-review & editing: HTJ, HGK, JH.
