AbstractBackground/AimsThe use of endoscopic intervention (EI) for acute biliary pancreatitis (ABP) remains controversial because the severity of biliary obstruction/cholangitis/pancreatitis is not reflected in the indications for early EI (EEI).
MethodsA total of 148 patients with ABP were included to investigate 1) the differences in the rate of worsening cholangitis/pancreatitis between the EEI group and the early conservative management (ECM) group, especially for each severity of cholangitis/pancreatitis, and 2) the diagnostic ability of imaging studies, including endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), to detect common bile duct stones (CBDSs) in the ECM group.
ResultsNo differences were observed in the rate of worsening cholangitis between the EEI and ECM groups, regardless of the severity of cholangitis and/or the existence of impacted CBDSs. Among patients without impacted CBDSs and moderate/severe cholangitis, worsening pancreatitis was significantly more frequent in the EEI group (18% vs. 4%, <i>p</i>=0.048). In patients in the ECM group, the sensitivity and specificity for detecting CBDSs were 73% and 98%, respectively, for EUS, whereas the values were 13% and 92%, respectively, for magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
INTRODUCTIONAcute biliary pancreatitis (ABP) is a major cause of acute pancreatitis, similar to an alcoholic etiology. Clinically, ABP is characterized by the coexistence of the following conditions: acute pancreatitis, biliary obstruction, and/or acute cholangitis. Therefore, treatment strategies, including endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) for the removal of common bile duct stones (CBDSs), seem to be determined on the basis of the clinical severity of each of the above-mentioned conditions.
According to previous reports [1,2], ERCP may be unnecessary for almost half of the patients with ABP because of the large percentage of CBDSs that pass through the major papilla immediately after the onset of ABP. However, some patients with ABP need to immediately undergo ERCP to avoid clinical deterioration. In addition, after clinical improvement, residual CBDSs need to be removed using ERCP to prevent the recurrence of ABP. In other words, for the management of ABP, it is essential to determine whether ERCP is necessary or not in the ŌĆ£acute phaseŌĆØ and in the ŌĆ£remission phaseŌĆØ. ERCP in the acute phase, namely early endoscopic intervention (EEI), should be performed in patients with biliary obstruction and/or cholangitis, as indicated by current guidelines and the Cochrane systematic review [3ŌĆō6]. For ERCP in the remission phase, namely elective endoscopic intervention (elective EI), it should be performed only if CBDSs are detected using initial imaging studies, including computed tomography (CT), or additional imaging studies, such as endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), after clinical improvement.
In the above-mentioned situations, some issues with respect to the management of ABP remain controversial. First, the indications for EEI described in the guidelines may be inconclusive because the severity of biliary obstruction, cholangitis, and pancreatitis are not reflected, although the performance of EEI in clinical practice is generally determined on the basis of the severity of these clinical factors. Second, the optimal imaging modality for determining the need for elective EI after clinical improvement has not been specified in the guidelines. Therefore, we conducted this retrospective study to elucidate the two above-mentioned issues concerning ABP by reviewing our experience with treating patients with ABP.
MATERIALS AND METHODSPatientsThis study was approved by the Sendai City Medical Center institutional review board (registration no. 2016-42). Of 632 consecutive patients who were admitted to our medical center with a diagnosis of acute pancreatitis between January 2010 and December 2015, 148 patients retrospectively diagnosed with ABP were included in this study. On the basis of the diagnostic criteria of acute pancreatitis in the 2015 Japanese Guidelines [3], a diagnosis of acute pancreatitis requires two of the following three features: 1) abdominal pain associated with acute pancreatitis, 2) elevated serum levels of pancreatic enzymes, and 3) presence of acute pancreatitis detected on CT on admission (initial CT). The severity of acute pancreatitis was evaluated on the basis of the 2015 Japanese Guidelines criteria [3]. In this study, a diagnosis of ABP was made on the basis of the 2010 Japanese Guidelines criteria [7], and patients with other causes of acute pancreatitis, including autoimmune pancreatitis, alcohol abuse, pancreatic cancer, and chronic pancreatitis, were excluded. In addition, the severity of acute cholangitis associated with ABP was determined on the basis of the severity assessment criteria for acute cholangitis in the Tokyo Guidelines 2013/2018 (TG13/TG18) [8,9].
Treatment strategy for patients with acute biliary pancreatitisAll procedures in this study were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. In our experience at our medical center, patients with ABP generally underwent EEI when initial examinations detected the following: 1) cholangitis, especially moderate/severe cholangitis, and 2) impacted CBDSs in the major papilla [10], namely the severe type of biliary obstruction. In the case of persistent or worsening hyperbilirubinemia without cholangitis, namely non-emergency biliary obstruction, prompt elective EI was considered depending on the degree of hyperbilirubinemia and/or pancreatitis. For patients who underwent early conservative management (ECM), prompt elective EI was considered when cholangitis and/or obstructive jaundice became exacerbated.
Of the patients who underwent ECM, those with CBDSs detected on the initial CT underwent elective EI after the pancreatitis/cholangitis had improved. In addition, patients without CBDSs detected on the initial CT underwent EUS and/or MRCP to detect possible CBDSs.
Outcome measuresWe determined two main outcome measures in this study. First, to evaluate the value of EEI on the clinical course during hospitalization, the 148 total patients were classified into two groups according to the treatment strategy: EEI group and ECM group. Thereafter, we investigated the differences in the rates of worsening cholangitis/pancreatitis between the two groups, especially for each severity of biliary obstruction/cholangitis/pancreatitis on admission. Second, to clarify the optimal imaging modality for detecting residual CBDSs, we investigated the diagnostic ability of EUS or MRCP to detect CBDSs in patients without CBDSs detected on the initial CT.
Definition of early endoscopic interventionTo reflect our clinical practice, EEI was defined as an intervention that met the following criteria: 1) ERCP performed within 24 h after the first visit to our hospital, and 2) ERCP performed within the daytime of the visit to our hospital if patients with ABP visited our hospital from 0:00 to 17:00, or ERCP performed on the day after the visit to our hospital if patients with ABP visited our hospital from 17:00 to 0:00.
Definition of definitive common bile duct stonesTo evaluate the diagnostic ability of imaging modalities to detect CBDSs, we defined the following patients as having definitive CBDSs: 1) patients with CBDSs determined with ERCP during hospitalization and 2) patients without CBDSs determined with additional imaging modalities except for ERCP, followed by the development of recurrent biliary diseases, including ABP, within 12 months after the initial hospitalization for ABP despite having a history of cholecystectomy. In addition, CBDSs were defined to include bile duct sludges because these can also cause gallstone pancreatitis, similar to CBDSs.
In contrast, the following patients were defined as having no definitive CBDSs: 1) patients in whom CBDSs were not detected with ERCP in addition to other imaging methods, 2) patients in whom CBDSs were not detected with ERCP despite being detected with any imaging modality, and 3) patients in whom CBDSs were not detected with MRCP and/or EUS in addition to the initial CT, together with the absence of recurrent biliary diseases during surveillance. Patients who did not undergo additional imaging studies to detect CBDSs despite the non-detection of CBDSs on the initial CT were defined as those with an indeterminate diagnosis of CBDSs.
In addition, we defined patients categorized into 1) or 3) as those having spontaneously passed CBDSs ŌĆ£on admissionŌĆØ. For patients categorized into 2), their CBDSs were considered as having spontaneously passed ŌĆ£after admissionŌĆØ. However, when the diagnostic ability of imaging studies for detecting CBDSs was assessed, patients in 2) were defined as having false diagnoses, in order to avoid overestimation of the diagnostic abilities.
For the diagnostic abilities of the respective imaging methods for detecting CBDSs, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy to detect CBDSs were investigated.
Definitions of worsening cholangitis/pancreatitis after admissionWorsening cholangitis or pancreatitis was defined as present if it occurred within 5 days after admission. Worsening cholangitis was defined as follows: 1) progression from no cholangitis/mild cholangitis to moderate cholangitis, 2) progression from moderate to severe cholangitis, or 3) an increase in the number of dysfunctioning organs/systems, as described in the TG13/TG18 guidelines, in patients diagnosed with severe cholangitis on admission [8,9]. However, even if patients had one of the factors used for the determination of severe cholangitis (thrombocytopenia [platelet count <100,000/┬ĄL], serum creatinine level >2.0 mg/dL, and prothrombin time-international normalized ratio >1.5), cholangitis was not determined to be severe when it did not meet the definition of moderate cholangitis. This is because those factors are unlikely to be due to severe cholangitis in the above-mentioned situation (e.g., they may be preexisting factors).
In addition, pancreatitis was defined as ŌĆ£worseningŌĆØ when 1) worsening from mild to severe pancreatitis occurred after admission, or 2) the prognostic factor score increased from <3 to Ōēź3 after admission and/or the CT grade increased after the diagnosis of severe pancreatitis on admission.
Endoscopic proceduresA radial-array echoendoscope (GF-UM 2000 or GF-UE260-AL5; Olympus Co., Tokyo, Japan) or a convex-array echoendoscope (GF-UCT260, Olympus Co.) was used to perform EUS. For the processing of images from EUS, the EU-ME1 or EU-ME2 ultrasonographic system (Olympus Co.) was used.
With respect to ERCP, the standard contrast injection technique was initially used with a 4-Fr cannula (PR-104Q-1 or PR-109Q-1, Olympus Co.). In cases with no coagulation abnormalities, CBDSs were removed using balloons and/or baskets after endoscopic sphincterotomy when CBDSs were detected using cholangiography and/or intraductal ultrasonography (IDUS). Conversely, patients with coagulation abnormalities underwent EEI without endoscopic sphincterotomy for biliary drainage using a 7-Fr plastic tube stent, or elective EI after the improvement of coagulopathy. When filling defects indicative of CBDSs were not observed in the bile duct on cholangiography, IDUS was performed to detect residual CBDSs.
Statistical analysisAll statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (IBM SPSS Statistics 21; IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). PearsonŌĆÖs Žć2 or FisherŌĆÖs exact test was used for categorical variables, whereas StudentŌĆÖs t-test or the Mann-Whitney U-test (with the distribution of variables shown as interquartile ranges [IQRs]) was used for continuous data. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTSPatient characteristicsOf the 148 patients, 88 were men (59%) and the mean age was 70 ┬▒ 14 years (range, 32ŌĆō96 years). From the findings of the initial CT, the median common bile duct diameter was 8.7 mm (IQR, 7.0ŌĆō10.7 mm). CBDSs were detected in 48 patients (32%), and impacted CBDSs in the major papilla were detected in 21 patients (14%). On admission, 115 patients (78%) were diagnosed with cholangitis (mild: 80, moderate: 34, severe: 1), and 39 patients (26%) were diagnosed with severe pancreatitis. During a median hospitalization period of 15 days (IQR: 11ŌĆō22 days), one patient (0.7%) died of severe pancreatitis. (Table 1)
Clinical courses of the 148 patients with acute biliary pancreatitisAll 148 patients with ABP underwent initial CT. Of the 47 patients who underwent EEI, 33 were diagnosed with definitive CBDSs using EEI. Of the 101 patients who underwent ECM, 19 patients with CBDSs detected on initial CT underwent elective EI without additional imaging studies, resulting in a definitive diagnosis of CBDSs in 12 patients.
Of the 82 patients who underwent ECM because the initial CT did not detect CBDSs, 69 underwent EUS and/or MRCP. CBDSs were detected with those modalities in 12 of 69 patients, and definitive CBDSs were detected using elective EI in 9 of 12 patients. Of the 57 patients without CBDSs detected using EUS/MRCP, 10 underwent elective EI and 47 underwent surveillance without undergoing elective EI.
Finally, 98 patients (66%) underwent ERCP (EEI: 47, elective EI: 51), and 62 patients (42%) were diagnosed with definitive CBDSs on ERCP. Of the 47 patients who underwent surveillance without ERCP because EUS and/or MRCP did not detect CBDSs, 3 patients developed recurrent biliary diseases caused by CBDSs despite having a history of cholecystectomy. After adding these 3 patients, 65 patients (44%) were finally determined to have definitive CBDSs. In addition, the remaining 80 patients, except for 3 patients with an indeterminate diagnosis of CBDSs, were shown to have spontaneously passed CBDSs (on admission: 66, after admission: 14), and the percentage of those patients from the total study population was 54%. (Fig. 1)
Differences in baseline characteristics between the early endoscopic intervention and early conservative managemen groupsEEI was performed at a median of 7 h after the first visit (IQR, 3ŌĆō18 h). The success rate of EEI for biliary drainage was 98% (46/47). In one patient with a surgically altered anatomy, EEI failed and CBDSs were surgically removed. Complete clearance of CBDSs during the first ERCP procedure was achieved in 41 patients (87%), and complete clearance within three ERCP procedures was achieved in all 46 patients, excluding the single patient who underwent surgery. Pancreatitis/cholangitis-associated death did not occur in this group.
Fifty-one patients in the ECM group underwent elective EI at a median of 8 days after the first visit (IQR, 4ŌĆō16 days). One patient (an 82-year-old woman) with severe pancreatitis died of pancreatitis despite receiving intensive care, and this patient was not indicated for EEI owing to the absence of both cholangitis and impacted CBDSs. Finally, pancreatitis and/or cholangitis improved with ECM in 99% (100/101) of the patients in this group.
Laboratory data except for serum calcium levels on admission were similar between the EEI and ECM groups. From the findings of the initial CT, the common bile duct diameter and the detection rate of CBDSs or impacted CBDSs were significantly higher in the EEI group than in the ECM group. The percentage of patients with moderate/severe cholangitis and that of patients with severe pancreatitis did not differ between the two groups. The hospitalization period was significantly longer in the ECM group than in the EEI group (median: 17 vs. 13 days, p=0.021). (Table 2)
Rate of worsening cholangitis/pancreatitisThe rates of worsening cholangitis were similar between the EEI and ECM groups (15% vs. 18%, p=0.426). Among the 21 patients with impacted CBDSs, although there were no significant differences in the rate of worsening cholangitis between the two groups, one of the four patients with impacted CBDSs who did not undergo EEI because of advanced age and some comorbidities developed septic shock due to worsening cholangitis on day 3 of hospitalization. In patients with no cholangitis, mild cholangitis, and moderate cholangitis on admission, the rate of worsening cholangitis seemed similar between the EEI and ECM groups.
Patients in the EEI group showed a higher tendency of developing worsening pancreatitis than those in the ECM group (15% vs. 6%, p=0.073). In patients with impacted CBDSs and/or moderate/severe cholangitis, the rate of worsening pancreatitis was similar between the EEI and ECM groups. Meanwhile, in patients without impacted CBDSs and moderate/severe cholangitis, the rate of worsening pancreatitis was significantly higher in the EEI group than in the ECM group (18% vs. 4%, p=0.048). The rates of worsening of mild and severe pancreatitis were not significantly different between the two groups. (Table 3)
Diagnostic ability of computed tomography, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, or endoscopic ultrasonography for detecting common bile duct stonesA total of 145 patients who underwent initial CT, except for 3 patients with an indeterminate diagnosis of CBDSs, were analyzed to clarify the diagnostic ability of initial CT to detect CBDSs. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy of initial CT to detect CBDSs were 55% (36/65), 86% (69/80), 77% (36/47), 70% (69/98), and 72% (108/145), respectively.
For the diagnostic ability of EUS or MRCP to detect CBDSs in 69 patients who underwent ECM, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy to detect CBDSs were 73% (8/11), 98% (44/45), 89% (8/9), 94% (44/47), and 93% (52/56), respectively, for EUS, whereas the values were 13% (1/8), 92% (24/26), 33% (1/3), 77% (24/31), and 74% (25/34), respectively, for MRCP. In addition, we calculated the above-mentioned diagnostic ability parameters of EUS or MRCP in 22 patients who underwent both EUS and MRCP. The sensitivity for the detection of CBDSs was 60% (3/5) for EUS and 0% (0/5) for MRCP (Fig. 2). (Table 4)
DISCUSSIONIn the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guidelines for choledocholithiasis [4], ABP is categorized as having an intermediate probability of choledocholithiasis (10ŌĆō50%) because many patients with ABP have been reported to have spontaneously passed stones. Therefore, it is necessary to clarify the appropriate indications for EEI to avoid unnecessary ERCP, and thereby reduce post-ERCP complications and cost. In clinical practice, the need for EEI seems to be determined on the basis of the severity of biliary obstruction, cholangitis, and pancreatitis, and/or the detection of CBDSs using clinical laboratory tests and/or initial imaging studies. Therefore, this study provides more concrete implications with respect to performing EEI than those described in published guidelines.
This study did not indicate the clinical implications of performing EEI according to the severity of cholangitis. Therefore, ECM may be acceptable even for patients with ABP involving acute cholangitis, on a case-by-case basis. In other words, a wait-and-see approach, with attention paid to the deterioration of cholangitis, may be allowed for ABP involving cholangitis. For impacted CBDSs, this study could also not indicate the efficacy of EEI. As most patients with impacted CBDSs underwent EEI, it may be difficult to determine which of the two clinical plans is better for those patients. However, it should be noted that all patients with impacted CBDSs who underwent EEI showed good clinical courses, and that one of the four patients with impacted CBDSs who underwent ECM developed acute obstructive suppurative cholangitis 3 days after the initial visit.
However, if the above-mentioned indications for EEI are absent, EEI should not be performed because of the significantly high rate of worsening pancreatitis (18% vs. 4%, p=0.048). Recently, a multicenter, randomized clinical trial in patients with severe ABP without cholangitis has clarified the lack of benefit of EEI for those patients [11], although there may be patients with severe pancreatitis for whom EEI is effective (e.g., those with cholangitis and/or biliary obstruction, described as indications for EEI by the guidelines) [3ŌĆō5]. As some patients with ABP who undergo EEI can theoretically develop worsening pancreatitis owing to the addition of post-ERCP pancreatitis, EEI should be avoided in the absence of reasonable grounds. In contrast, and interestingly, there were no differences in the rate of worsening pancreatitis in patients with the above-mentioned indications for EEI, including impacted CBDSs, between the EEI and ECM groups. This might imply that EEI may have prevented the worsening of pancreatitis in those patients.
In addition, this study indicates that EUS may be superior to MRCP for the detection of residual CBDSs after ECM in patients with ABP in whom the initial CT could not detect CBDSs. The sensitivity to detect residual CBDSs was much higher for EUS than for MRCP (EUS: 73%, MRCP: 13%). Verma et al. reviewed five reports of randomized controlled studies to determine the ability of EUS and MRCP to detect ŌĆ£ordinaryŌĆØ CBDSs [12]. They reported that the two modalities have excellent detection rates for CBDSs, with no statistically significant differences. However, it has been reported that CBDSs with sizes Ōēż5 mm can be overlooked by MRCP [13] and that the detection rate of EUS is not affected by the size of CBDSs [14]. A recent meta-analysis with a head-to-head comparison [15] reported that EUS has statistically better diagnostic accuracy and sensitivity for detecting CBDSs than MRCP. For patients with ABP, only a few reports have demonstrated the high diagnostic abilities of the two modalities for detecting CBDSs associated with ABP [2,16ŌĆō18]. Although EUS or MRCP is likely to be selected for detecting residual CBDSs depending on the availability at each facility, patients with ABP having no indications for EEI should undergo EUS to detect residual CBDSs if EUS is available.
This study had several limitations. First, this was a retrospective, single-center study. Therefore, the results of this study need to be verified by future studies with a prospective, multicenter, large-sample validation cohort. Second, the determination of definitive CBDSs using ERCP or clinical courses can result in false diagnoses. Although this may be a small possibility for ERCP because we always use IDUS if the presence of CBDSs is uncertain [19,20], it may not always be correct to determine CBDSs as having spontaneously passed based on the clinical courses. Third, the diagnostic ability of CT/EUS/MRCP to detect CBDSs may have been underestimated because some patients with ABP may have spontaneously passed CBDSs ŌĆ£after admissionŌĆØ, namely between the time of undergoing CT/EUS/MRCP and the time of undergoing ERCP [17]. Fourth, it can sometimes be difficult to discriminate the exacerbation of pancreatitis from that of cholangitis, especially when common clinical factors used for determining the severities of cholangitis and pancreatitis were found to be worsening after admission. Fifth, contrary to the strategy for performing elective ERCP described in this study, there were 10 patients who underwent elective ERCP owing to prolonged liver dysfunction and other reasons despite the lack of findings suggestive of CBDSs on EUS/MRCP. Despite these limitations, the results of this study are notable and the indications for EEI should be further considered. Moreover, EUS was shown to have a better sensitivity than MRCP for detecting CBDSs in patients with ABP.
In conclusion, EEI should be avoided in the absence of moderate/severe cholangitis and impacted CBDSs because of the high rate of worsening pancreatitis. In addition, EUS can contribute to more accurate evaluations for determining whether elective EI should be performed after ECM for ABP than can MRCP.
NOTESAuthor Contributions
Conceptualization: Sho Hasegawa, Shinsuke Koshita, Yoshihide Kanno, Takahisa Ogawa, Toshitaka Sakai, Hiroaki Kusunose, Kensuke Kubota, Atsushi Nakajima, Yutaka Noda, Kei Ito
Data curation: SH, SK
Formal analysis: SH, SK, TS, HK
Investigation: SH, SK, YK, TO
Supervision: KI
Writing ŌĆō original draft: SH, SK
Writing ŌĆō review & editing: YK, TO, TS, HK, KK, AN, YN, KI
AcknowledgmentsWe thank Brian K. Breedlove, Associate Professor, Graduate School of Science, Tohoku University, for English proofreading.
Fig.┬Ā1.Flowchart of this study. Of the 148 patients with acute biliary pancreatitis (ABP), 47 underwent early endoscopic intervention (EEI) using endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) at a median of 7 h after admission, and the remaining 101 patients underwent early conservative management (ECM). Finally, 98 patients (66%) underwent ERCP (early: 47, elective: 51), and 62 patients (42%) were diagnosed as having definitive common bile duct stones (CBDSs) with ERCP. After adding three patients who developed recurrent biliary diseases, including ABP, after being found to have no CBDSs during hospitalization, a total of 65 patients were finally diagnosed as having definitive CBDSs. CBDSs, common bile duct stones; CT, computed tomography; ECM, early conservative management; EEI, early endoscopic intervention; ERCP, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; EUS, endoscopic ultrasound; MRCP, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. 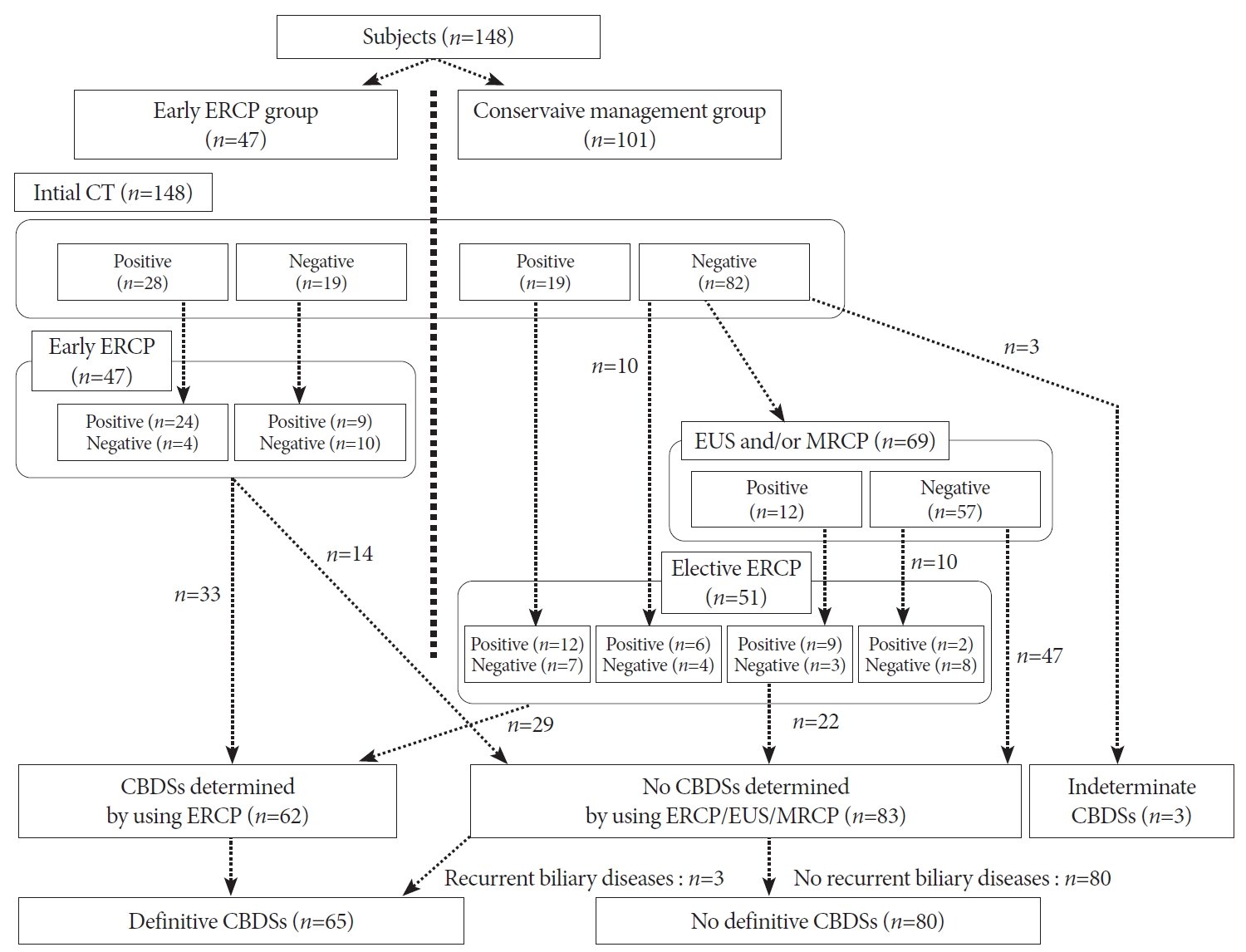
Fig.┬Ā2.A 55-year-old man with acute biliary pancreatitis was admitted to our hospital. He underwent early conservative management owing to the absence of both cholangitis and common bile duct stones (CBDSs) determined with computed tomography. After the improvement of pancreatitis, he underwent magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) for detecting residual CBDSs. (A) MRCP. No CBDSs were detected with MRCP (white arrow: common bile duct). (B) EUS. Two CBDSs with sizes <5 mm were detected with EUS (yellow arrowhead: two CBDSs, white arrow: common bile duct). (C) Endoscopic view of the second duodenum. Two CBDSs were detected with endoscopic retrograde cholangiography with intraductal ultrasonography, and those stones were removed from the common bile duct by using a balloon catheter (yellow arrowhead: a bile duct stone removed from the common bile duct). 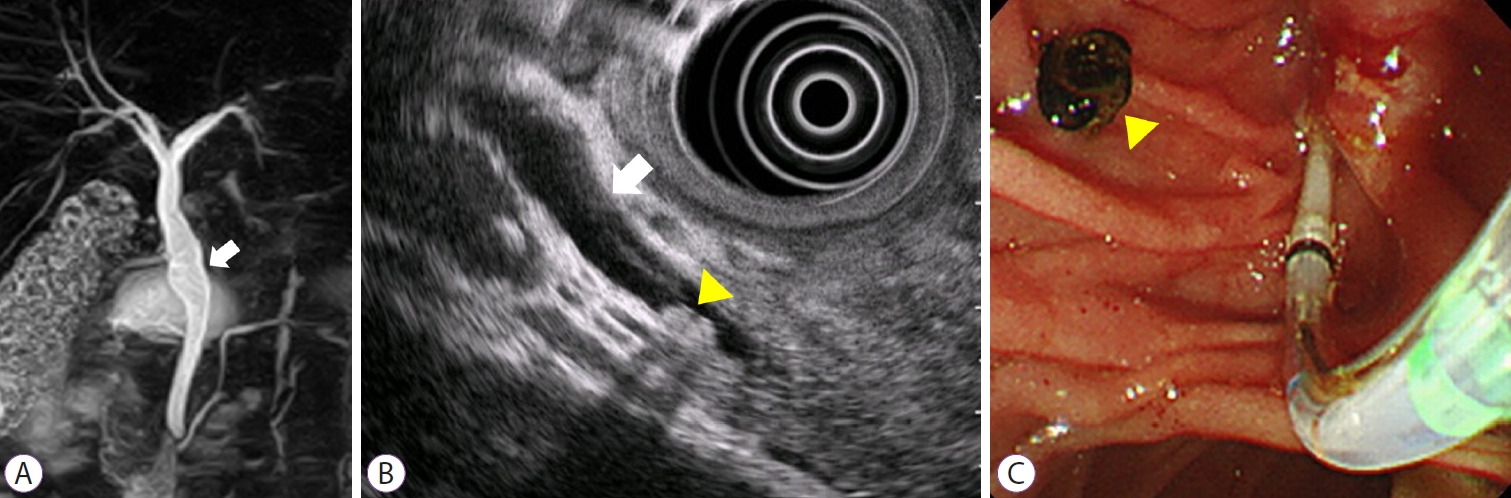
Table┬Ā1.Baseline Characteristics of the 148 Patients
CBD, common bile duct; CBDSs, common bile duct stones; CT, computed tomography; ERCP, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; IQR, interquartile range; PF, prognostic factor; SD, standard deviation; TG, Tokyo guidelines. Table┬Ā2.Differences in the Baseline Characteristics between EEI- and ECM-Group Alb, albumin; AMY, amylase; Ca, calcium; CT, computed tomography; CBD, common bile duct; CBDSs, common bile duct stones; Cr, creatinine; CRP, C-reactive protein; ECM, early conservative management; EEI, early endoscopic intervention; ERCP, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; IQR, interquartile range; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PF, prognostic factor; Plt, platelet; PT-INR, prothrombin time international normalized ratio; SD, standard deviation; TG, Tokyo guidelines; WBC, white blood cell Table┬Ā3.The Rate of Worsening of Acute Cholangitis and Pancreatitis Table┬Ā4.Diagnostic ability for the detection of CBDSs by using CT, MRCP, or EUS REFERENCES1. Maple JT, Ben-Menachem T, Anderson MA, et al. The role of endoscopy in the evaluation of suspected choledocholithiasis. Gastrointest Endosc 2010;71:1ŌĆō9.
2. Anderloni A, Galeazzi M, Ballare M, et al. Early endoscopic ultrasonography in acute biliary pancreatitis: a prospective pilot study. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:10427ŌĆō10434.
3. Yokoe M, Takada T, Mayumi T, et al. Japanese guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis: Japanese guidelines 2015. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2015;22:405ŌĆō432.
4. ASGE Standards of Practice committee, Buxbaum JL, Abbas Fehmi SM, et al. ASGE guideline on the role of endoscopy in the evaluation and management of choledocholithiasis. Gastrointest Endosc 2019;89:1075ŌĆō1105.
5. Williams E, Beckingham I, El Sayed G, Gurusamy K, Webster G, Young T. Updated guideline on the management of common bile duct stones (CBDS). Gut 2017;66:765ŌĆō782.
6. Tse F, Yuan Y. Early routine endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography strategy versus early conservative management strategy in acute gallstone pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;(5):CD009779.
7. Kimura Y, Arata S, Takada T, et al. Gallstone-induced acute pancreatitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2010;17:60ŌĆō69.
8. Kiriyama S, Takada T, Strasberg SM, et al. TG13 guidelines for diagnosis and severity grading of acute cholangitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2013;20:24ŌĆō34.
9. Kiriyama S, Kozaka K, Takada T, et al. Tokyo guidelines 2018: diagnostic criteria and severity grading of acute cholangitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2018;25:17ŌĆō30.
10. Acosta JM, Katkhouda N, Debian KA, Groshen SG, Tsao-Wei DD, Berne TV. Early ductal decompression versus conservative management for gallstone pancreatitis with ampullary obstruction: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg 2006;243:33ŌĆō40.
11. Schepers NJ, Hallensleben NDL, Besselink MG, et al. Urgent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with sphincterotomy versus conservative treatment in predicted severe acute gallstone pancreatitis (APEC): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020;396:167ŌĆō176.
12. Verma D, Kapadia A, Eisen GM, Adler DG. EUS vs MRCP for detection of choledocholithiasis. Gastrointest Endosc 2006;64:248ŌĆō254.
13. Kondo S, Isayama H, Akahane M, et al. Detection of common bile duct stones: comparison between endoscopic ultrasonography, magnetic resonance cholangiography, and helical-computed-tomographic cholangiography. Eur J Radiol 2005;54:271ŌĆō275.
14. Sugiyama M, Atomi Y. Endoscopic ultrasonography for diagnosing choledocholithiasis: a prospective comparative study with ultrasonography and computed tomography. Gastrointest Endosc 1997;45:143ŌĆō146.
15. Meeralam Y, Al-Shammari K, Yaghoobi M. Diagnostic accuracy of EUS compared with MRCP in detecting choledocholithiasis: a meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy in head-to-head studies. Gastrointest Endosc 2017;86:986ŌĆō993.
16. Liu CL, Fan ST, Lo CM, et al. Comparison of early endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in the management of acute biliary pancreatitis: a prospective randomized study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005;3:1238ŌĆō1244.
17. Lee SL, Kim HK, Choi HH, et al. Diagnostic value of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography to detect bile duct stones in acute biliary pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2018;18:22ŌĆō28.
18. Cavdar F, Yildar M, Tellio─¤lu G, Kara M, Tilki M, Titiz M─░. Controversial issues in biliary pancreatitis: when should we perform MRCP and ERCP? Pancreatology 2014;14:411ŌĆō414.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
