CME for
KSGE members
Lee, Irani, and Chon: Nightmare of straight-type plastic stent migration into the peripheral bile duct: what is my savior?
Quiz
A 76-year-old female patient was referred to our hospital complaining of high fever (up to 39.5 Ā°C). She was receiving chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer at another hospital and had undergone endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) for biliary drainage using a plastic stent (straight-type, 8.5 FrĆ7 cm, Boston Scientific) 29 days prior. Laboratory examination revealed elevated total bilirubin level (3.41 mg/dL), aspartate transaminase level (135 IU/L), alanine transaminase level (161 IU/L), gamma-glutamyl transferase level (234 IU/L), and C-reactive protein level (129.84 mg/L). Abdominopelvic computed tomography revealed proximal migration of the previously placed stent with a distal bile duct stricture due to pancreatic head cancer ( Fig. 1). ERCP was performed in order to remove the migrated stent. In our first attempt, we utilized a stone extraction balloon catheter to sweep the proximal part of the plastic stent. However, longitudinal force exerted by the stone extraction balloon catheter was inadequate due to the straight-type biliary plastic stent being located too peripherally, and this led to failure to remove the stent. Then, a standard basket and rat-tooth forceps were used to grab the stent or stent flap for removal of the migrated stent, but it was unsuccessful as well. The stent had migrated proximally into the bile duct. What is the most favorable treatment option?
Answer 
A digital single-operator cholangioscopy (D-SOC) system (SpyGlass DS; Boston Scientific) was used and the D-SOC was advanced through the guidewire in the direction of the migrated plastic stent ( Fig. 2A). Next, the distal flap of the plastic biliary stent was captured using a SpyGlass retrieval basket (Boston Scientific) ( Fig. 2Bā D, Supplementary Video 1). The stent was withdrawn slowly under direct endoscopic visualization using D-SOC and fluoroscopic guidance ( Fig. 2E, F). Thereafter, plastic biliary stent (7 Fr, double pigtail) placement and endoscopic nasobiliary drainage were performed. Biliary plastic stent placement via ERCP is widely used to treat obstructive jaundice due to malignant stricture. 1 The incidence of proximal migration of biliary plastic stents has been reported to be 3.1% to 4.9%, 2-5 and the success rate of stent retrieval was approximately 88% in the first attempt. 5,6 Traditionally, stone extraction balloon catheters, stone retrieval baskets, forceps, and Soehendra stent retrievers have been used to retrieve proximally migrated stents. If classical endoscopic methods fail, secondary complications, such as obstruction, infection, and perforation caused by the remaining stent, may occur. With the recent introduction of D-SOC, SpyGlass retrieval baskets can be used to precisely grasping the flaps of migrated plastic stents under direct visualization. This enables the removal of stents without complications. Therefore, D-SOC-guided plastic stent removal into the deep peripheral bile duct should be considered if the other methods fail.
Fig.Ā 1.
Abdominal computed tomography findings. (A, B) A proximally migrated straight-type biliary plastic stent (black open arrows) is observed in the coronal view and axial view. (C) Proximally migrated plastic straight-type biliary stent (black open arrow) and pancreatic mass (white arrow) are observed in the axial view. 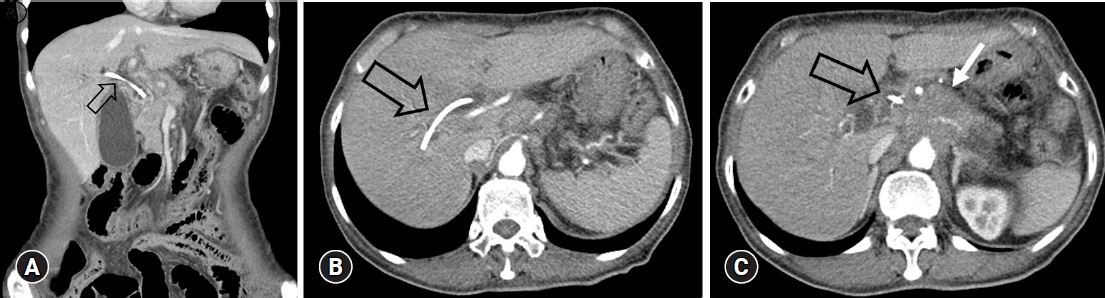
Fig.Ā 2.
Process of proximally migrated straight-type plastic biliary stent removal using digital single-operator cholangioscopy (D-SOC). (A) In D-SOC, the scope (white open arrow) is inserted through the guidewire to assist with the direction of the migrated stent (black open arrow), as noted in the fluoroscopic image. (B) A flap is observed at the distal end of a plastic biliary stent under D-SOC. (C, D) The flap on the distal part of the plastic stent is captured using a SpyGlass retrieval basket (white arrow). (E, F) The migrated plastic biliary stent is removed by slowly withdrawing the D-SOC and duodenoscope simultaneously. 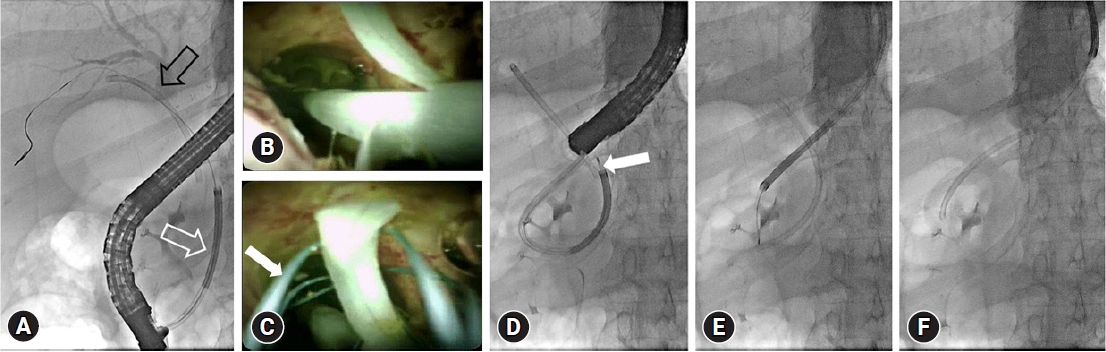
|
|











