AbstractThe field of artificial intelligence is rapidly evolving, and there has been an interest in its use to predict the risk of lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer. Accurately predicting lymph node invasion may result in fewer patients undergoing unnecessary surgeries; conversely, inadequate assessments will result in suboptimal oncological outcomes. This narrative review aims to summarize the current literature on deep learning for predicting the probability of lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer, highlighting areas of potential application and barriers that may limit its generalizability and clinical utility.
INTRODUCTIONColorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with the number of cases estimated to increase to 3.2 million by 2040.1,2 Population-based CRC screenings can improve patient outcomes through early diagnosis and treatment, but have led to higher incidences of T1 (early) CRC.3,4 T1 CRC can be grouped based on the invasion depth into the mucosa (Tis), superficial submucosa (T1a <1,000 ┬Ąm submucosal invasion), and deep submucosa (T1b Ōēź1,000 ┬Ąm submucosal invasion). Although endoscopic resection is the treatment modality of choice for superficial colorectal neoplasms,5,6 further surgical resection may be recommended based on the presence of risk factors after a full histological evaluation of the resected specimen.7-9 This is due to the risk of lymph node metastasis (LNM) in T1 CRC. The histological risk factors include lymphovascular invasion, tumor budding, and histological grade in addition to the depth of invasion.10-15 However, the risk of LNM in T1 CRC is estimated to be between 6% to 14%,16-19 which indicates that the postoperative morbidity and mortality associated with surgery for T1 CRC is avoidable.20,21 As such, accurately predicting the depth of invasion on the initial colonoscopy and consistent and precise histological specimen reports are crucial in patients with T1 CRC.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been extensively studied in the context of polyp detection and, to a lesser extent, in the prediction of polyp histology during colonoscopy.22-24 Computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) systems that perform these functions are commercially available. However, predicting the risk of LNM is a complex task in CAD systems. Unlike CAD systems for the detection and prediction of polyp histology, determining the presence or absence of LNM in T1 CRC requires the input of different forms of data from various sources. These include predicting the depth of invasion during colonoscopy, analyzing resected specimens for histology, and interpreting radiological images from cross-sectional imaging, which are sometimes performed in the context of rectal cancer.
This narrative review aimed to summarize the current evidence and clinical applications of AI in the prediction of LNM in T1 CRC. The role of AI in colonoscopy and histological examination will be examined, and the merits and limitations of its role in predicting LNM in T1 CRC will be discussed.
METHODSA systematic search of the PubMed (Medline), Embase, and IEEE Xplore electronic databases was performed from the database inception up to November 18, 2022 (Fig. 1). The key search terms were AI, deep learning (DL), machine learning (ML), computer-aided diagnosis, T1 colon cancer, T1 rectal cancer, T1 CRC, and LNM. Electronic searches were supplemented with manual searches of the references of all the retrieved studies to identify other relevant publications. Only studies published in English were included in this review.
AI PREDICTION OF THE DEPTH OF INVASION IN T1 CRC DURING ENDOSCOPYThe depth of invasion is a known risk factor for LNM in T1 CRC. Traditionally, predicting the depth of invasion during colonoscopy depends largely on the availability and use of image-enhanced endoscopy (IEE), or without magnification,33-38 to accurately classify the neoplastic potential of polyps based on the surface pattern and vessel appearance. The overall morphological appearance of colorectal tumors is also a known predictor of the depth of invasion, with features such as large size, pseudo-depressed or depressed areas, and the presence of large nodules indicative of a higher risk for deep and multifocal submucosal invasion.39,40 However, IEE systems may not be readily available at all centers. Furthermore, structured training and experience are required even when these resources are available, resulting in wide interobserver variability.41,42
Early studies incorporating AI for CAD in CRC focused on differentiating invasive cancers from the normal colonic mucosa or adenomas.43 Some of these studies utilized endocytoscopy and confocal laser endomicroscopy with encouraging results,44,45 but were limited in that they could not accurately assess the depth of invasion of T1 CRC. Endocytoscopy and confocal laser endomicroscopy may not be practical in wide-scale applications, as additional training and highly specialized equipment are required, even with a CAD function to alleviate the need for training. These imaging modalities require the endoscopist to focus on a very small area of the tumor at a time, making them time-consuming and labor-intensive to use in clinical settings. Furthermore, the CAD function in these studies was not trained to consider the macroscopic features of the tumor of interest. Lui et al.46 trained an AI image classifier that could predict curative endoscopic resection in large colonic tumors with an overall accuracy of 85.5% and an area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve of 0.837, which was similar to that of a senior endoscopist who had performed more than 200 IEE colonoscopies. However, the image classifier was unsuitable for clinical use because it required a senior endoscopist to manually map the region of interest before the AI image classifier could make a prediction.
To overcome these technical difficulties, Luo et al.47 added a tumor-localization branch to a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) model developed by modifying the GoogLeNet architecture. This enabled the CNN model to highlight the tumor area by exploiting the localization features of class activation maps while preserving useful information that lies outside the tumor area. The classification branch then predicts the histological invasiveness in the tumor area. The AI-enhanced attention-guided white-light colonoscopy (AEWL) model achieved an overall accuracy of 91.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 89.6%ŌĆō92.4%), with an AUROC curve of 0.970 (95% CI, 0.962ŌĆō0.978) in predicting non-invasive and superficially invasive colorectal tumors, which in this study were defined as Tis and T1a lesions. The corresponding sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were 91.2, 91.0, 87.6, and 93.7%, respectively. The performance of the AEWL model was evaluated against that of experienced endoscopists using white-light and IEE with magnification. The results of this study showed that the accuracy of the AEWL model in estimating the depth of CRC invasion was comparable to that of experienced endoscopists (91.1% vs. 92.6%). However, when discriminating between T1b CRC and superficially invasive CRC, the sensitivity and AUROC of the AEWL model were 51.5% and 0.637, respectively. When images of advanced CRC were added to the training dataset, the sensitivity and AUROC improved by 65.3% and 0.729, respectively. The authors hypothesized that the surface signatures of T1b and advanced CRC may share certain similarities; hence, the addition of advanced CRC images to the training dataset could improve the performance of the DL model.
The AEWL model is a fully automated CAD system that utilizes non-magnified white-light images during colonoscopy, circumventing the need for IEE images in the training of CAD systems. This is arguably clinically more useful, as white light colonoscopy is the most widely available imaging modality compared with electronic or dye-based IEE. Tokunaga et al.48 developed a CAD system using non-magnified white-light colonoscopy images and a single-shot multibox detector to differentiate advanced CRC or CRC with submucosal invasion Ōēź1,000 ┬Ąm, which are not amenable to endoscopic resection, from superficially invasive and mucosal lesions, which could be resected endoscopically. The accuracy and AUROC curves for predicting endoscopically resectable lesions in this study were 90.3% and 0.913, respectively. The CAD system had similar sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy as expert endoscopists and was found to be superior to trainee endoscopists. However, in a subgroup analysis of T1b CRC, the rate of correct diagnosis was only 51.2%, although this outperformed that of the trainees and experts (31.5% and 41.1%; p<0.01, and p=0.047, respectively). This drop-off in accuracy in T1b CRC was similar to that described earlier for the AEWL model.47
In a retrospective study using non-magnified white-light images, Ito et al.49 built a CNN specifically to assist in the diagnosis of T1b CRC. The authors augmented the data by adding flipped and rotated images, with up to six times as many images as in the original being used as input for training the CNN, while excluding images deemed unsuitable for learning in each augmentation process. A 3-fold cross validation method was used, which excluded images that were altered for data augmentation. Using these methods, the study reported an accuracy of 81.2% and an AUROC of 0.871 for differentiating T1b from T1a and Tis CRC. The reported sensitivity and specificity were 89% and 68%, respectively. In a separate study by Nakajima et al.,50 non-magnified white-light images of early stage CRC labelled only with the T-stage were used to train a CNN that could output a probability level for T1b CRC. Data augmentation was applied with rotation, resizing, saturation, and exposure adjustments to increase the number of training images from the original. The CNN model was assessed on an independent test dataset from an external hospital, with a threshold of 95% used to predict T1b CRC (at least one image with a probability score of >0.95 was considered a positive predictor for T1b CRC). The specificity, which was the main outcome of this study, was 87%. This was superior to the specificity of the two novice endoscopists (48% and 22%, respectively) but inferior to that of expert endoscopists (100% and 96%, respectively). The CAD system accuracy in predicting T1b CRC was 78% and 85% for CRC Ōēż20 mm and >20 mm, respectively. A major limitation of this study was that the test dataset did not include T1a lesions; thus, we were unable to demonstrate the CAD system effectivity at differentiating the threshold depth of submucosal invasion, which defines T1a and T1b CRC.
In a study by Lu et al.,51 white-light and IEE images were combined into image pairs for training Endo-CRC, a 2-model neural network consisting of white-light and IEE convolution branches, along with a feature fusion convolution block and classifier. Testing of the Endo-CRC system was conducted on video clips that ranged from 10 to 19 seconds and comprised white-light and IEE images from an external test dataset. Based on the test results from 35 videos, the authors reported an accuracy of 100% in differentiating unresectable deeply invasive T1 CRC from resectable colorectal tumors. The speed of the Endo-CRC system was at least 21 image pairs per second, based on a real-time video analysis. While the results were encouraging when tested on colonoscopy videos, the Endo-CRC system is likely not ready for routine clinical use, as our experience has shown that video output from high-definition colonoscopy systems requires a processing speed of approximately 50 frames per second.24 Table 1 summarizes the current studies using AI to predict the depth of invasion in TI-CRC.46-51
AI IN PREDICTION OF LNM ON HISTOLOGYFollowing the endoscopic resection of T1 CRC, the histological specimen was carefully examined for risk factors indicating the possibility of LNM to determine if the endoscopic resection was curative. In a clinical setting, the risk of LNM may be considered at the point of diagnosis of T1 CRC on endoscopy, when a decision on endoscopic resectability needs to be made, or after endoscopic resection, when the clinician needs to decide whether the patient requires additional surgery based on the histological findings of the resected specimen. The histological factors predicting LNM after endoscopic resection include the depth of invasion, tumor budding, histological grade, and lymphovascular invasion.10-12,52 However, the interobserver agreement between pathologists in T1 CRC for lymphovascular invasion has been shown to vary. This is further exacerbated by the fact that immunostaining may not be routinely performed in all centers.53,54 Furthermore, interobserver agreement has been reported to be even lower in the assessment of the depth of invasion55 and tumor budding.56-58 There is also conflicting evidence on the magnitude of the risk of LNM posed by the depth of invasion, with studies suggesting that this may not be a crucial risk factor for LNM.59-61 DL models have been studied in this context to provide an objective ŌĆ£2nd readerŌĆØ function and for automated processing of histology slides in T1 CRC for predicting LNM.
Conventional light microscopy is considered the ŌĆ£gold standardŌĆØ in surgical pathology62,63; however, progress and innovations in digital imaging inspired by telepathology have led to the development of whole-slide imaging (WSI).64,65 WSI enables the digitalization of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) slides, which can be stored, shared, and viewed by different pathologists. The standardization of H&E staining into a uniform digital format also means that DL algorithms can be deployed in histological image analysis.66 This has led to the development of AI systems that can robustly process large amounts of WSI for the diagnosis and prediction of outcomes in CRC.67 One study reported an AUROC curve of 0.988 for accurately diagnosing CRC on WSI, which was higher than that of expert pathologists (0.970) and could potentially be generalized for clinical use.68 To overcome the tedious and time-consuming process of examining specimens for abnormal areas on histology, Gupta et al.69 examined the use of DL models for classification and localization to determine regions of interest for pathologists to focus on in CRC. The study reported an AUROC curve of 0.97 using a pretrained Inception-v3 model and an AUROC curve of 0.99 with a customized Inception-ResNet-v2 Type 5 (IR-v2 Type 5) model. The prediction of LNM in CRC using DL models and WSI has also been studied.70 In a German study of 2,431 patients from the German DACHS cohort, a slide-based artificial intelligence predictor (SBAIP) score was combined with a logistic regression analysis of clinical data and externally tested in a different cohort of patients. The SBAIP had an AUROC curve of 0.612 in predicting LNM in CRC; although, it must be noted that the study included different stages of CRC and the small number of T1 CRC precluded a subgroup analysis.
Kudo et al. conducted a multicenter study to evaluate the accuracy of an artificial neural network (ANN) model for predicting LNM in patients with T1 CRC.71 Demographic and clinical data, such as patient age, sex, tumor size, location, and morphology, were combined with pathological data, such as lymphovascular invasion and grade, from 3,134 patients who had undergone endoscopic or surgical resection for T1 CRC in Japan. These clinicopathological data were used to train the ANN model, which was assessed against the current United States (US)13,14,72 and the Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (JSCCR) 10 guidelines during external validation on a test dataset. The ANN model identified patients with LNM after initial endoscopic resection with an AUROC curve of 0.84, which outperformed the US (AUROC curve 0.77, p=0.005) and Japanese (AUROC curve 0.61, p<0.001) guidelines. However, histological factors, such as the depth of invasion and tumor budding, were not included in the training of the ANN model.
In a retrospective study of 316 patients with T1 CRC, Kang et al.73 evaluated the performance of the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) model with the JSCCR guidelines for prediction LNM.10 The ML model incorporates information from immunohistochemical staining and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), which mediate local host antitumor immunity, with histological factors such as depth of submucosal invasion, tumor budding, histological grade, and lymphovascular invasion. The AUROC curve in the validation set showed better accuracy in predicting LNM using the LASSO model than using the Japanese guidelines (0.765 vs. 0.518, p=0.003). An earlier Dutch study identified histological factors of lymphovascular invasion, Haggitt level 4 invasion, muscularis mucosa type B, poorly differentiated clusters, and tumor budding as differentiating factors for predicting LNM in patients with pedunculated T1 CRC.74 Using these histological factors, the LASSO model was evaluated in a large multicenter Dutch cohort of 708 patients with pedunculated T1 CRC and showed an AUROC of 0.83, which was superior to conventional models based on American/European and Japanese guidelines (AUROC curves of 0.67 and 0.64, respectively). Takamatsu et al.75 conducted a retrospective single-center study in which histological images from 397 patients with T1 CRC were used for supervised ML. The AUROC curve for the prediction of LNM was 0.938, using an optimal cut-off sensitivity of 80.0% and specificity of 94.5% in the ML model. Cross validation was performed with repeated random subsampling to generate 12 validation datasets, with an average AUROC curve of 0.822 (95% CI, 0.767ŌĆō0.938). More recently, an attention-based DL model by Song et al.76 achieved an AUROC of 0.844 for predicting LNM in the test set for patients with a submucosal invasion of 1,000 to 2,000 ┬Ąm. When the performance of this model was compared against the prediction of LNM using the JSCCR guidelines,10 the DL model was able to avoid 16.1% of unnecessary additional surgeries in this group of patients while not missing any patients with LNM.
To date, most studies on DL for predicting the risk of LNM on WSI have analyzed full histological specimens post-endoscopic or surgical resection. However, in a study by Kasahara et al.,77 ML was used to train a model to predict the risk of LNM in biopsy specimens. The investigators analyzed the morphological features of cell nuclei extracted from WSI to create an LNM risk model with the aim of directing patients with T1 CRC to appropriate treatments based on their risk of LNM determined from pre-treatment biopsy specimens. The study demonstrated an accuracy of 80% to 85% in predicting LNM on biopsy specimens. In a separate study conducted in two large population-based cohorts of patients with T1 and T2 CRC, a DL system was used to direct human pathology experts to areas deemed to contain features highly predictive of LNM in the WSI of the primary tumor and surrounding tissues.78 An interesting finding from this study was that the hybrid application of human observers and DL-identified inflamed adipose tissue was the highest predictor of LNM. This has not been described as a known histological risk factor for LNM in T1 CRC and highlights the potential for using AI to discover new biomarkers for CRC progression. Table 2 summarizes the current studies using AI in histopathology for predicting the risk of LNM in T1 CRC.70,71,73,75-78
DL has also been studied for the detection of microsatellite instability, mismatch repair genes, and other genetic alterations in CRC.79-81 This may highlight CRC biomarkers that can predict LNM when integrated into clinical decision-making tools. However, these DL models are still in the early stages of development and require extensive external validation. They also do not directly address the issue of LNM prediction in T1 CRC and are thus beyond the scope of this review.
CURRENT LIMITATIONS OF STUDIES ON AI IN T1 CRCDespite the advances and reported outcomes of AI studies in predicting of depth of invasion and LNM to guide the management of T1 CRC, there are still major gaps that limit its generalizability and clinical application. DL, a subbranch of the ML field, is the most commonly used tool in the literature on AI and colonoscopy.25,82 In this method, multiple linear and nonlinear processing units are arranged in a deep architecture to extract useful information automatically and construct a model that generates the required output. DL models perform these tasks without requiring predefined features, which is characteristic of conventional ML techniques.25 The DL studied during colonoscopy is well suited for simple tasks such as polyp detection or polyp histology, as data from a single source of input (colonoscopy image projected from the processor) are passed through multiple layers in a neural network to produce a narrow output that is often binary (polyp or no polyp; hyperplastic or neoplastic, respectively). However, clinical decision-making regarding LNM in T1 CRC depends on more than one factor. The analysis of endoscopy videos during colonoscopy for depth of invasion, histopathology slides or reports on risk factors of LNM, radiological images and clinical and demographic characteristics of the population, mean that more than one source of input is available in T1 CRC cases (Fig. 2). No single DL model can accommodate the processing of all these information sources, such as how a clinician processes information during decision-making to obtain the required output in the presence or absence of LNM. Moreover, DL models require a large number of cases to build.83 When the relevant specimens available for analyses are limitedŌĆöfor instance, in T1b CRC47-50,77ŌĆöthe results of the models may be inconclusive at best, and in some instances investigators may need to rely on an ML method instead77 because of its inherent limitations.
The avoidance of overfitting a DL model and its reliability is highly dependent on the quality, number, and variability of the images used for training, as well as the demographic and clinical features of the populations from which the data are gathered. Most published studies on DL in T1 CRC acknowledge the limitations of their datasets, as the number of high-quality images of T1 CRC datasets is smaller and may lack detailed annotations compared to polyp databases used in training DL models for polyp detection and characterization. This is also reflected in the studies that may not contain sufficient or even any T1a CRC in the datasets used for validation, which prevents subgroup analysis and comparisons from obtaining clinically meaningful data for differentiating T1a from T1b CRC. Furthermore, the training, validation, and test datasets are often derived from populations in the same geographical location and are sometimes split from the same overall dataset in a single institution, leading to a risk of selection bias and overfitting due to the probability of significant overlaps in clinicopathological features when the baseline population is identical.25
In addition, most studies evaluating CAD systems in T1 CRC during endoscopy are retrospective and utilize still images, which may be difficult to translate into clinical practice when the real-time prediction of the LNM risk during colonoscopy is required. When video clips are used for validation, the speed of the DL model may be inadequate for routine clinical use in high-definition systems. Although recent studies have almost uniformly assessed DL models (as opposed to conventional ML and other statistical methods) for the prediction of LNM in T1 CRC, there remains a lack of standardization in reporting methodologies and results, which may make meaningful comparisons of different CAD systems and meta-analyses of the available data difficult. Studies on AI that address key questions31 regarding its use in T1 CRC, as well as a minimum reporting standard27,28,30 such as that required for randomized controlled trials, are needed to overcome this discrepancy.
Similarly, in the fields of DL and WSI, the quality of the WSI used as input for training DL models is crucial for its accuracy in predicting LNM in T1 CRC. Owing to the high dimensionality of the data, the original image may need to be downsized, where pixel information may be lost or broken down into multiple smaller patches for information extraction, which comes at the expense of spatial information.84 As highlighted in the section on histology, the variations in interobserver variability for tumor budding and depth of invasion among pathologists, coupled with the controversies surrounding the role of depth of invasion in predicting the actual risk of LNM, translate into uncertainty in the ŌĆ£ground truthŌĆØ and weight assignment in the training of DL models for use in predicting LNM from T1 CRC samples.
In practice, determining the risk of LNM in T1 CRC depends on the demographic and clinical profile of the patient, predicted depth of invasion prior to resection, detailed pathological assessment after resection, and preoperative lymph node staging on CT or MRIŌĆönot on any of these factors in isolation. The available literature on DL in T1 CRC focuses mainly on one of the aforementioned factors, with statistical regression or conventional ML models used to combine additional patient information in some studies. For a DL model to be accurate and clinically relevant, at least two of these factors must be incorporated. This involves the insertion of additional branches into ANN algorithms and the use of natural language processing to extract information from endoscopy, histology, and radiology reports,85 which is computationally expensive and technically demanding.
CONCLUSIONSThe field of DL in the management of T1 CRC is developing rapidly, with results showing its potential to accurately predict the depth of invasion and risk of LNM during endoscopy and pathological assessment. However, more data from external validation of independent samples from different centers, as well as further enhancements to DL models to integrate clinically significant information, are necessary before DL can be applied for routine clinical use.
Fig.┬Ā1.Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses diagram of the literature search. AI, artificial intelligence; CRC, colorectal cancer. 
Fig.┬Ā2.Schematic diagram illustrating varied sources of input and differing outputs to reach a clinical decision on lymph node metastasis (LNM) in T1 colorectal cancer (CRC). AI, artificial intelligence; ML, machine learning; NLP, natural language processing; WSI, whole slide imaging; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; LVI, lymphovascular invasion. 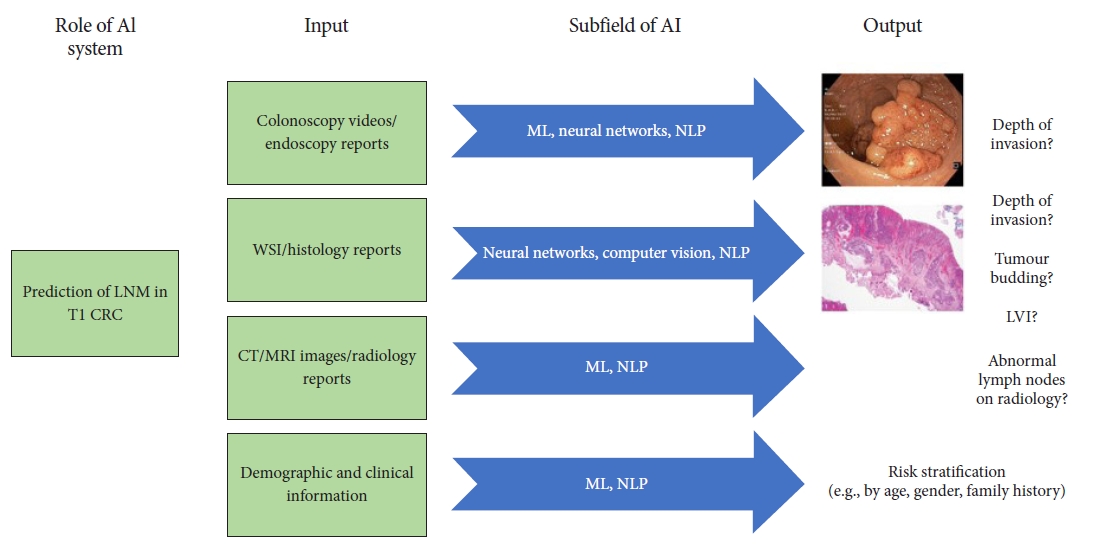
Table┬Ā1.Summary of studies using CAD during endoscopy to predict depth of invasion in CRC
CAD, computer-aided diagnostic; CRC, colorectal cancer; AI, artificial intelligence; PPV, positive predictive value; NPV, negative predictive value; AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic; CNN, Convolutional neural network; NBI, narrow-band imaging; WLI, white-light imaging; IEE, image-enhanced endoscopy. a) Prediction endoscopically curable lesions (includes sessile serrated adenomas, tubular adenoma with or without villous component, intramucosal adenocarcinoma, and T1a lesions). Table┬Ā2.Summary of studies using AI to determine risk of LNM on histology
AI, artificial intelligence; LNM, lymph node metastasis; PPV, positive predictive value; NPV, negative predictive value; AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic; CNN, convolutional neural network; CRC, colorectal cancer; PTS, peritumoral stroma; ANN, artificial neural network; LASSO, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; RFC, random forest classifier; IHC, immunohistochemistry; -, results not reported in study. b) Study included endoscopically resected, with or without additional surgical resection and lymph node dissection. c) Prediction of lymph node metastasis based on US guidelines (National Comprehensive Cancer Network). REFERENCES1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71:209ŌĆō249.
2. Xi Y, Xu P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl Oncol 2021;14:101174.
3. Bretthauer M, Kaminski MF, L├Ėberg M, et al. Population-based colonoscopy screening for colorectal cancer: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2016;176:894ŌĆō902.
5. Draganov PV, Wang AY, Othman MO, et al. AGA Institute Clinical Practice Update: endoscopic submucosal dissection in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;17:16ŌĆō25.
6. Pimentel-Nunes P, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Ponchon T, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 2015;47:829ŌĆō854.
7. Dykstra MA, Gimon TI, Ronksley PE, et al. Classic and novel histopathologic risk factors for lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis Colon Rectum 2021;64:1139ŌĆō1150.
8. Niimi K, Fujishiro M, Kodashima S, et al. Long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms. Endoscopy 2010;42:723ŌĆō729.
9. Saito Y, Uraoka T, Yamaguchi Y, et al. A prospective, multicenter study of 1111 colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2010;72:1217ŌĆō1225.
10. Hashiguchi Y, Muro K, Saito Y, et al. Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (JSCCR) guidelines 2019 for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 2020;25:1ŌĆō42.
11. Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum. Japanese classification of colorectal, appendiceal, and anal carcinoma: the 3d English edition [secondary publication]. J Anus Rectum Colon 2019;3:175ŌĆō195.
12. Tateishi Y, Nakanishi Y, Taniguchi H, et al. Pathological prognostic factors predicting lymph node metastasis in submucosal invasive (T1) colorectal carcinoma. Mod Pathol 2010;23:1068ŌĆō1072.
13. Glynne-Jones R, Wyrwicz L, Tiret E, et al. Rectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2017;28(suppl_4):iv22ŌĆōiv40.
14. Benson AB, Venook AP, Al-Hawary MM, et al. Rectal cancer, version 2.2018, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2018;16:874ŌĆō901.
15. Bosch SL, Teerenstra S, de Wilt JH, et al. Predicting lymph node metastasis in pT1 colorectal cancer: a systematic review of risk factors providing rationale for therapy decisions. Endoscopy 2013;45:827ŌĆō834.
16. Ebbeh├Ėj AL, J├Ėrgensen LN, Krarup PM, et al. Histopathological risk factors for lymph node metastases in T1 colorectal cancer: meta-analysis. Br J Surg 2021;108:769ŌĆō776.
17. Nascimbeni R, Burgart LJ, Nivatvongs S, et al. Risk of lymph node metastasis in T1 carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Dis Colon Rectum 2002;45:200ŌĆō206.
18. Yamamoto S, Watanabe M, Hasegawa H, et al. The risk of lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 2004;51:998ŌĆō1000.
19. Zong Z, Li H, Hu CG, et al. Predictors of lymph-node metastasis in surgically resected T1 colorectal cancer in Western populations. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf) 2021;9:470ŌĆō474.
20. Vermeer NC, Backes Y, Snijders HS, et al. National cohort study on postoperative risks after surgery for submucosal invasive colorectal cancer. BJS Open 2018;3:210ŌĆō217.
21. Ichimasa K, Kudo SE, Miyachi H, et al. Current problems and perspectives of pathological risk factors for lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer: systematic review. Dig Endosc 2022;34:901ŌĆō912.
22. Hassan C, Spadaccini M, Iannone A, et al. Performance of artificial intelligence in colonoscopy for adenoma and polyp detection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2021;93:77ŌĆō85.
23. Sivananthan A, Nazarian S, Ayaru L, et al. Does computer-aided diagnostic endoscopy improve the detection of commonly missed polyps?: a meta-analysis. Clin Endosc 2022;55:355ŌĆō364.
24. Li JW, Chia T, Fock KM, et al. Artificial intelligence and polyp detection in colonoscopy: use of a single neural network to achieve rapid polyp localization for clinical use. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;36:3298ŌĆō3307.
25. Li JW, Ang TL. Colonoscopy and artificial intelligence: bridging the gap or a gap needing to be bridged? Artif Intell Gastrointest Endosc 2021;2:36ŌĆō49.
26. Chen H, Sung JJ. Potentials of AI in medical image analysis in gastroenterology and hepatology. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;36:31ŌĆō38.
27. Collins GS, Moons KG. Reporting of artificial intelligence prediction models. Lancet 2019;393:1577ŌĆō1579.
28. CONSORT-AI and SPIRIT-AI Steering Group. Reporting guidelines for clinical trials evaluating artificial intelligence interventions are needed. Nat Med 2019;25:1467ŌĆō1468.
29. Nagendran M, Chen Y, Lovejoy CA, et al. Artificial intelligence versus clinicians: systematic review of design, reporting standards, and claims of deep learning studies. BMJ 2020;368:m689.
30. Rivera SC, Liu X, Chan AW, et al. Guidelines for clinical trial protocols for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the SPIRIT-AI Extension. BMJ 2020;370:m3210.
31. Ahmad OF, Mori Y, Misawa M, et al. Establishing key research questions for the implementation of artificial intelligence in colonoscopy: a modified Delphi method. Endoscopy 2021;53:893ŌĆō901.
32. Li JW, Ang TL. Narrow-band imaging. In: Chiu PW, Sano Y, Uedo N, Singh R, editors. Endoscopy in early gastrointestinal cancers, volume 1: diagnosis. Singapore: Springer Singapore; 2021. p. 111ŌĆō119.
33. Sano Y, Tanaka S, Kudo SE, et al. Narrow-band imaging (NBI) magnifying endoscopic classification of colorectal tumors proposed by the Japan NBI Expert Team. Dig Endosc 2016;28:526ŌĆō533.
34. Ito R, Ikematsu H, Murano T, et al. Diagnostic ability of Japan Narrow-Band Imaging Expert Team classification for colorectal lesions by magnifying endoscopy with blue laser imaging versus narrow-band imaging. Endosc Int Open 2021;9:E271ŌĆōE277.
35. Hewett DG, Kaltenbach T, Sano Y, et al. Validation of a simple classification system for endoscopic diagnosis of small colorectal polyps using narrow-band imaging. Gastroenterology 2012;143:599ŌĆō607.
36. Kaltenbach T, Anderson JC, Burke CA, et al. Endoscopic removal of colorectal lesions-recommendations by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2020;158:1095ŌĆō1129.
37. Desai M, Kennedy K, Aihara H, et al. External validation of blue light imaging (BLI) criteria for the optical characterization of colorectal polyps by endoscopy experts. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;36:2728ŌĆō2734.
38. Bisschops R, East JE, Hassan C, et al. Advanced imaging for detection and differentiation of colorectal neoplasia: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) guideline: update 2019. Endoscopy 2019;51:1155ŌĆō1179.
39. Ishigaki T, Kudo SE, Miyachi H, et al. Treatment policy for colonic laterally spreading tumors based on each clinicopathologic feature of 4 subtypes: actual status of pseudo-depressed type. Gastrointest Endosc 2020;92:1083ŌĆō1094.
40. Vosko S, Shahidi N, Sidhu M, et al. Optical evaluation for predicting cancer in large nonpedunculated colorectal polyps is accurate for flat lesions. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;19:2425ŌĆō2434.
41. Smith SCL, Siau K, Cannatelli R, et al. Training methods in optical diagnosis and characterization of colorectal polyps: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc Int Open 2021;9:E716ŌĆōE726.
42. Klare P, Haller B, Wormbt S, et al. Narrow-band imaging vs. high definition white light for optical diagnosis of small colorectal polyps: a randomized multicenter trial. Endoscopy 2016;48:909ŌĆō915.
43. Takemura Y, Yoshida S, Tanaka S, et al. Computer-aided system for predicting the histology of colorectal tumors by using narrow-band imaging magnifying colonoscopy (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2012;75:179ŌĆō185.
44. Takeda K, Kudo SE, Mori Y, et al. Accuracy of diagnosing invasive colorectal cancer using computer-aided endocytoscopy. Endoscopy 2017;49:798ŌĆō802.
45. ┼×tef─ānescu D, Streba C, C├ór┼Ż├ón─ā ET, et al. Computer aided diagnosis for confocal laser endomicroscopy in advanced colorectal adenocarcinoma. PLoS One 2016;11:e0154863.
46. Lui TK, Wong KK, Mak LL, et al. Endoscopic prediction of deeply submucosal invasive carcinoma with use of artificial intelligence. Endosc Int Open 2019;7:E514ŌĆōE520.
47. Luo X, Wang J, Han Z, et al. Artificial intelligence-enhanced white-light colonoscopy with attention guidance predicts colorectal cancer invasion depth. Gastrointest Endosc 2021;94:627ŌĆō638.
48. Tokunaga M, Matsumura T, Nankinzan R, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis system using only white-light endoscopy for the prediction of invasion depth in colorectal cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 2021;93:647ŌĆō653.
49. Ito N, Kawahira H, Nakashima H, et al. Endoscopic diagnostic support system for cT1b colorectal cancer using deep learning. Oncology 2019;96:44ŌĆō50.
50. Nakajima Y, Zhu X, Nemoto D, et al. Diagnostic performance of artificial intelligence to identify deeply invasive colorectal cancer on non-magnified plain endoscopic images. Endosc Int Open 2020;8:E1341ŌĆōE1348.
51. Lu Z, Xu Y, Yao L, et al. Real-time automated diagnosis of colorectal cancer invasion depth using a deep learning model with multimodal data (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2022;95:1186ŌĆō1194.
52. Ang TL, Lim JF, Chua TS, et al. Clinical guidance on endoscopic management of colonic polyps in Singapore. Singapore Med J 2022;63:173ŌĆō186.
53. Barel F, Auffret A, Cariou M, et al. High reproducibility is attainable in assessing histoprognostic parameters of pT1 colorectal cancer using routine histopathology slides and immunohistochemistry analyses. Pathology 2019;51:46ŌĆō54.
54. Kojima M, Puppa G, Kirsch R, et al. Blood and lymphatic vessel invasion in pT1 colorectal cancer: an international concordance study. J Clin Pathol 2015;68:628ŌĆō632.
55. Kouyama Y, Kudo SE, Miyachi H, et al. Practical problems of measuring depth of submucosal invasion in T1 colorectal carcinomas. Int J Colorectal Dis 2016;31:137ŌĆō146.
56. Hacking S, Nasim R, Lee L, et al. Whole slide imaging and colorectal carcinoma: a validation study for tumor budding and stromal differentiation. Pathol Res Pract 2020;216:153233.
57. Hacking S, Angert M, Jin C, et al. Tumor budding in colorectal carcinoma: an institutional interobserver reliability and prognostic study of colorectal adenocarcinoma cases. Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;43:151420.
58. Martin B, Sch├żfer E, Jakubowicz E, et al. Interobserver variability in the H&E-based assessment of tumor budding in pT3/4 colon cancer: does it affect the prognostic relevance? Virchows Arch 2018;473:189ŌĆō197.
59. Miyachi H, Kudo SE, Ichimasa K, et al. Management of T1 colorectal cancers after endoscopic treatment based on the risk stratification of lymph node metastasis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;31:1126ŌĆō1132.
60. Nakadoi K, Tanaka S, Kanao H, et al. Management of T1 colorectal carcinoma with special reference to criteria for curative endoscopic resection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;27:1057ŌĆō1062.
61. Zwager LW, Bastiaansen BA, Montazeri NS, et al. Deep submucosal invasion is not an independent risk factor for lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2022;163:174ŌĆō189.
62. Goacher E, Randell R, Williams B, et al. The diagnostic concordance of whole slide imaging and light microscopy: a systematic review. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:151ŌĆō161.
63. Koch LH, Lampros JN, Delong LK, et al. Randomized comparison of virtual microscopy and traditional glass microscopy in diagnostic accuracy among dermatology and pathology residents. Hum Pathol 2009;40:662ŌĆō667.
64. Mukhopadhyay S, Feldman MD, Abels E, et al. Whole slide imaging versus microscopy for primary diagnosis in surgical pathology: a multicenter blinded randomized noninferiority study of 1992 cases (pivotal study). Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:39ŌĆō52.
65. Weinstein RS, Holcomb MJ, Krupinski EA. Invention and early history of telepathology (1985-2000). J Pathol Inform 2019;10:1.
66. Ben Hamida A, Devanne M, Weber J, et al. Deep learning for colon cancer histopathological images analysis. Comput Biol Med 2021;136:104730.
67. Skrede OJ, De Raedt S, Kleppe A, et al. Deep learning for prediction of colorectal cancer outcome: a discovery and validation study. Lancet 2020;395:350ŌĆō360.
68. Wang KS, Yu G, Xu C, et al. Accurate diagnosis of colorectal cancer based on histopathology images using artificial intelligence. BMC Med 2021;19:76.
69. Gupta P, Huang Y, Sahoo PK, et al. Colon tissues classification and localization in whole slide images using deep learning. Diagnostics (Basel) 2021;11:1398.
70. Kwak MS, Lee HH, Yang JM, et al. Deep convolutional neural network-based lymph node metastasis prediction for colon cancer using histopathological images. Front Oncol 2021;10:619803.
71. Kudo SE, Ichimasa K, Villard B, et al. Artificial intelligence system to determine risk of T1 colorectal cancer metastasis to lymph node. Gastroenterology 2021;160:1075ŌĆō1084.
72. Labianca R, Nordlinger B, Beretta GD, et al. Early colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2013;24 Suppl 6:vi64ŌĆōvi72.
73. Kang J, Choi YJ, Kim IK, et al. LASSO-based machine learning algorithm for prediction of lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer. Cancer Res Treat 2021;53:773ŌĆō783.
74. Backes Y, Elias SG, Groen JN, et al. Histologic factors associated with need for surgery in patients with pedunculated T1 colorectal carcinomas. Gastroenterology 2018;154:1647ŌĆō1659.
75. Takamatsu M, Yamamoto N, Kawachi H, et al. Prediction of early colorectal cancer metastasis by machine learning using digital slide images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2019;178:155ŌĆō161.
76. Song JH, Hong Y, Kim ER, et al. Utility of artificial intelligence with deep learning of hematoxylin and eosin-stained whole slide images to predict lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer using endoscopically resected specimens; prediction of lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol 2022;57:654ŌĆō666.
77. Kasahara K, Katsumata K, Saito A, et al. Artificial intelligence predicts lymph node metastasis or risk of lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 2022;27:1570ŌĆō1579.
78. Brockmoeller S, Echle A, Ghaffari Laleh N, et al. Deep learning identifies inflamed fat as a risk factor for lymph node metastasis in early colorectal cancer. J Pathol 2022;256:269ŌĆō281.
79. Echle A, Grabsch HI, Quirke P, et al. Clinical-grade detection of microsatellite instability in colorectal tumors by deep learning. Gastroenterology 2020;159:1406ŌĆō1416.
80. Krause J, Grabsch HI, Kloor M, et al. Deep learning detects genetic alterations in cancer histology generated by adversarial networks. J Pathol 2021;254:70ŌĆō79.
81. Yamashita R, Long J, Longacre T, et al. Deep learning model for the prediction of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer: a diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol 2021;22:132ŌĆō141.
82. Li JW, Wang LM, Ang TL. Artificial intelligence-assisted colonoscopy: a narrative review of current data and clinical applications. Singapore Med J 2022;63:118ŌĆō124.
83. Yang CB, Kim SH, Lim YJ. Preparation of image databases for artificial intelligence algorithm development in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Clin Endosc 2022;55:594ŌĆō604.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
